Have you ever thought about how often farmers rely on guesswork? Weather patterns change fast. Pests show up without warning. Markets go up and down. The old ways are struggling to keep up. That’s where smart farming steps in.
Here’s something you might not expect: 45% of farmers today actually prefer to manage their work digitally, not by phone, not face-to-face, but through online tools. That’s a big shift.
So, how do we move from scattered notes and word-of-mouth advice to data-powered decisions? That’s what this article is about. Let’s break down what is smart farming, how it works, and why it’s not just for big farms anymore.
What Is Smart Farming?
It is not science fiction. It’s a way of using data, sensors, and automation to make farming more efficient. When people ask, “What is smart farming?” Think of it as turning your farm into a connected system. Your soil talks to your app, which talks to your irrigation pump, which talks to the weather forecast.
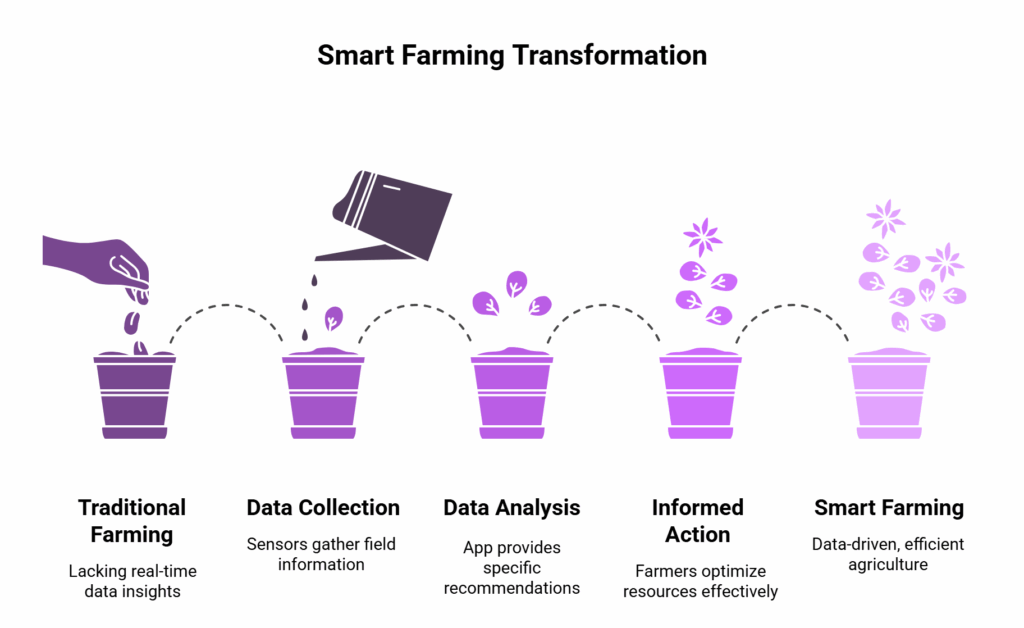
It connects all the pieces. Smart farming is built on smart farm technology like sensors, GPS, drones, and mobile apps. These tools help monitor everything, from soil moisture to pest activity. The goal is simple: grow more with less. Less waste, less water, less guesswork.
Smart farming apps are helping agriculture become more data-driven, improving both productivity and sustainability. Many of these tools are built through custom app development services tailored to the needs of modern farms.
How Does Smart Farming Work?
So, how it work? Think of it like a smart home, but for crops. It starts with sensors and devices on the field, soil sensors, weather monitors, drone cameras, and GPS-enabled tractors. These tools collect data about your land, crops, and environment in real time. That data is then sent to a smart farming app or dashboard.
Here’s what happens next:
- The app analyzes the data and sends back specific actions. For example, it might say, “You need 30% less water on field B today,” or “Field A has early signs of pest damage.”
- Farmers act on this advice, which saves time and cuts costs.
The system keeps learning. The more data it collects, the better its recommendations. If you’re planning a tech upgrade in agriculture, a custom mobile solution can make a real difference.
Key Technologies in Smart Farming
To understand smart agriculture deeply, you need to understand the technologies in smart farming that power it. Without these, the system falls apart.
1. Sensors and IoT Devices
Sensors are like the eyes and ears of your farm. Soil sensors measure moisture, temperature, and pH. Weather sensors tell you about wind, rainfall, and humidity. Livestock sensors monitor animal health.
These sensors are part of the Internet of Things (IoT). They collect data 24/7 and send it to the smart farming app. This means decisions are not based on instinct but on facts.
Scenario: A soil sensor alerts you that Field C is too dry. Your system then triggers automated irrigation, no manual checks needed.
2. Farm Management Software
This is the brain behind smart farming. The best smart farming software collects data from multiple sources and gives real-time reports. It can also track costs, crop cycles, inventory, and market prices.
You can also plan crop rotation, record pesticide use, and reorder supplies. With just a phone or tablet.
Tip: Choose a system that works offline too, in case of weak internet.
3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI powers the decision-making part of smart farming. Machine learning looks at past data to predict future outcomes. For example, it can forecast disease outbreaks, suggest planting dates, or optimize fertilizer use.
Case: An AI model tells you, based on 10 years of local weather and soil data, that this week is your best window to plant corn.
Integrating AI with IoT devices plays a key role in precision farming. Insights from AI in IoT applications show how connected devices and smart algorithms work together to monitor soil, weather, and crops in real time.
Smart Farming Benefits
Benefits both big and small farms. It’s not just about growth. It’s about doing more with less. You improve crop health, cut resource waste, and reduce manual labor. Here’s how that looks in real life.
1. Higher Yields With Less Waste
Using data, apps can pinpoint exactly what each crop needs and when. This prevents overwatering, over-fertilizing, or spraying healthy plants. Every input is used wisely.
Scenario: A farmer adds nutrients only where they are lacking, saving money and raising productivity.
2. Better Pest and Disease Control
Smart systems can detect diseases early using drone images or leaf sensors. Instead of spraying the whole farm, farmers treat just the affected area. This limits chemical use and crop damage.
Tip: Combine pest-detection AI with crop diaries to track recurring issues.
3. Market Timing and Demand Forecasting
Smart farming application tools can link your crop data to market trends. That means you plant and harvest based on what’s in demand. You waste less and sell more.
Example: Software predicts onion prices will drop in 6 weeks, so you schedule an early harvest.
Cost of Smart Farming: What to Expect
Let’s talk about real numbers. Cost depends on what tools you pick.
- Soil sensors: $250 per unit
- Drones: $1,500 to $5,000
- Farm management software: $50/month or $500/year
- Weather stations: $1,000
- Autonomous tractor: $100,000+
Example Calculation:
If you farm 100 acres and install:
- 5 sensors = $1,250
- 1 drone = $2,000
- Software = $500/year
Total first-year cost: $3,750 + labor training. This may seem high. But if you cut water use by 30% and raise yields by 20%, it pays back fast.
Behind every smart solution is a well-thought-out development strategy. Looking into the stages of AI product development helps ensure farming apps are built with scalability and efficiency in mind.
Smart Farming Solutions and Case Studies
There are more than 400 smart farming solutions active in sub-Saharan Africa alone. These contribute to promising smart farming statistics, helping smallholder farmers who grow nearly one-third of the world’s food.
In Kenya, small-scale farmers use AI tools like Virtual Agronomist and PlantVillage. For example, Sammy Selim followed crop advice from a Virtual Agronomist. His coffee yield jumped from 2.3 tonnes to 7.3 tonnes. Musau Mutisya used PlantVillage to spot pests early, avoid over-spraying, and improve plant health, clear smart farming advantages seen in action.
These tools work on basic phones too. That’s the future: powerful tools made simple, forming part of a larger smart farming infographic trend that highlights accessibility and impact.
To bring a smart farming app to life, working with experienced developers is key. Flexible options to hire a development team allow agricultural businesses to build tools that fit their operations.
Types of Smart Farming Applications
Have a smart farming app idea but not sure where to begin? You can contact the LITSLINK team to discuss the best approach for turning your concept into a functional, farm-ready solution.
Conclusion: Smarter Farms, Better Yields
Farming isn’t just soil and sweat anymore. It’s also data and decisions. And the numbers tell a clear story. Today, farm management software sees the most adoption at 21%. Next is remote sensing and precision agriculture hardware, sitting at 15%.
That’s not a trend. That’s a shift. A growing number of farmers want better tools, smarter tools. And now, they’re choosing a smart farming app over a phone call.
Use smart farming software that fits your crop, land, and budget. Whether you grow oranges in California or maize in Ohio, smarter farming gives you better control. And more control means more profit.
So, don’t wait until your neighbor’s field looks healthier than yours. Start small. Add one application. Check the smart farming cost. Build from there.
Better tools aren’t just for someone else’s farm. They’re for yours.
Ready to build your own custom smart farming software development solution?
Talk to LITSLINK today. Let’s turn your farming idea into a working digital product that grows your efficiency and yield.