Imagine building a high-performance web application that handles thousands of simultaneous connections with ease, all while using a framework you already know and love: Node.js.
Since its creation in 2009, Node.js has transformed web development as it has enabled developers to use JavaScript on the server-side for the first time. With its non-blocking, event-driven architecture, Node.js has become a go-to solution for real-time applications and microservices.
This article aims to walk you through Node.js architecture from A to Z, unveiling the secrets behind its speed, scalability, and efficiency. Whether you’re a seasoned developer or just starting out, you’ll gain valuable insights into why Node.js has captured the hearts of millions in the developer community.
One of the stepping stones to any web app development project is adopting a robust backend technology. Node.js has evolved as leading backend technology over the years because of its high flexibility and open-source nature.
Overview of Node.js
Launched in 2009 by Ryan Dahl, Node.js allows developers to use JavaScript (one of the 14 most popular languages) on the server side, revolutionizing the way web applications are built. Its non-blocking, event-driven architecture has made it a preferred choice for developing fast and scalable network applications. Find out 8 types of applications you can build with Node.js in our blog.
To see the impact of Node.js today, consider these statistics:
-
98% of Fortune 500 companies use Node.js in some capacity.
-
Canadian and American businesses that Node.js increased developers’ productivity by 70%.
-
85% of Node.js developers use it for web app development, and the other 43% use it for enterprise-grade applications.
-
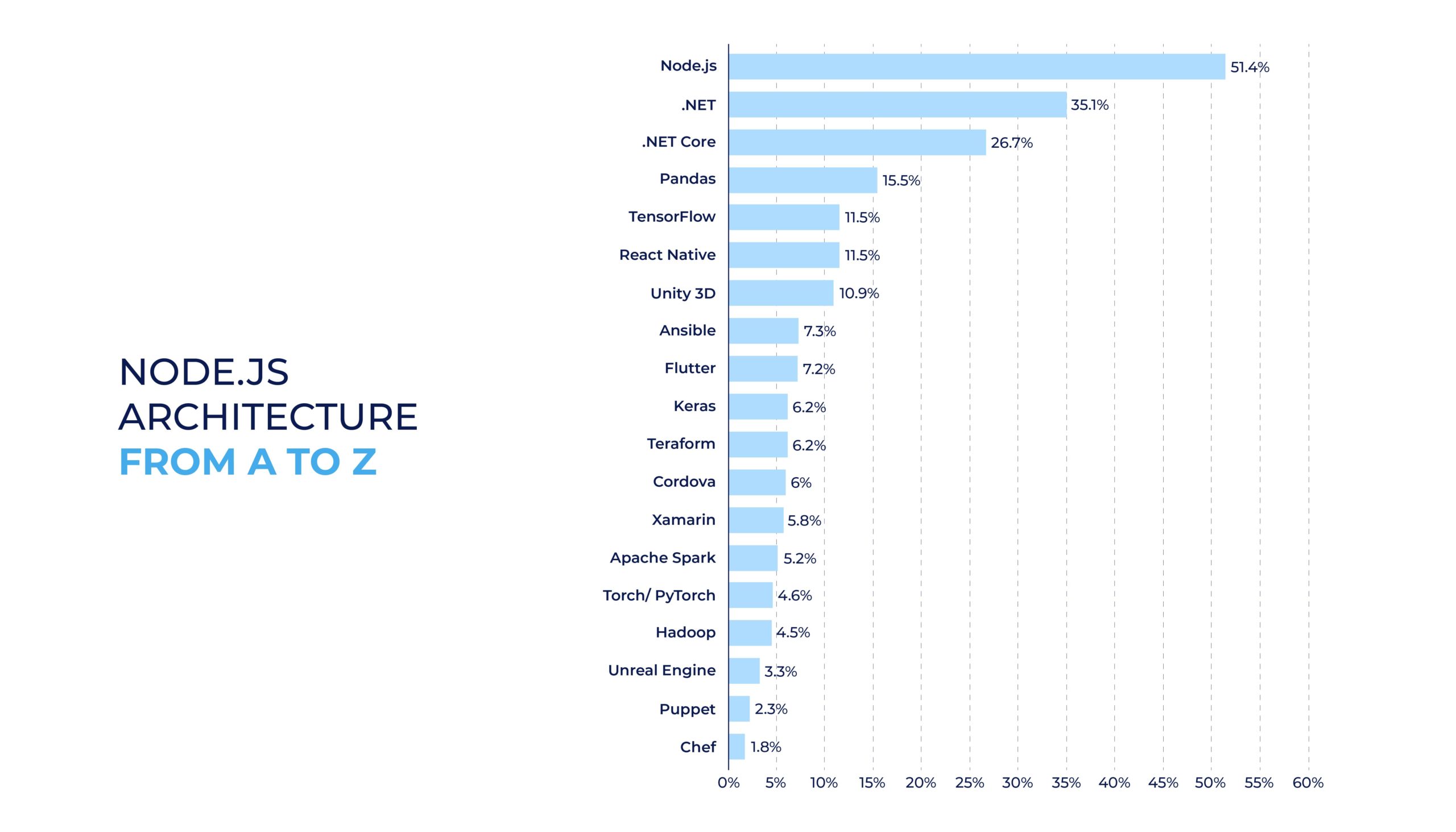
51.4% of developers regarded Node.js as the most-used tool earlier in 2020.
-
Node.js is used by at least 20 million websites as it reduces development costs by 58%.
-
Netflix, LinkedIn, PayPal, eBay, Uber, Nasa, X, and Walmart have adopted Node.js for their backend services.
Now, Node.js has become the first choice when it comes to developing web apps. NASA revealed that Node.js made migrating data from legacy databases to a cloud database effortless. Twitter reported a 30% faster launch time and quick loading on slower connections after employing Node.js. Indeed, this is also linked to the fact that JavaScript itself is one of the fastest programming languages. And Netflix migrated their backend from Java to Node.js which resulted in a decrease in startup time from 40 minutes to 60 seconds.
Node.js Use Cases
Node.js is suited best for applications where a continuous connection should be maintained between the browser and the server.
- Real-time Apps For Different Online Activities
Real-time apps usually include features like live chats, social media integration, ad servers, gamification, stock exchange features, etc. Node.js fits all the requirements in this ecosystem. Some of the examples of real-time apps that can be built with Node.js are VOIP (Voice Over Internet Protocol) apps, online gaming apps, instant messaging apps, ecommerce transactions like a stock exchange, document sharing app, and video conference apps.
- IoT Device Apps
Node.js has become one of the preferred solutions for enterprises and organizations seeking to build their private and public IoT systems. The main advantage of using Node.js is that it acquires less memory and requires fewer resources on the server-end. Node.js can process multiple concurrent requests and events emitted by thousands of devices on the network.
- Complex Single-page Applications (SPAs)
Node.js offers the ability to combine dynamic content and code features along with static file delivery of the SPA. The advantages of Node.js have been leveraged by such famous SPAs as Netflix and LinkedIn.
- Real-time Collaboration Tools
Node.js’s asynchronous and event-based architecture is a great fit for collaboration apps.
- Real-time Chats
Node.js provides everything needed for building real-time chats of any complexity. It makes it easy to implement server-side events and push notifications.
- Streaming Apps
Thanks to its native Stream API, Node.js is excellent for the development of streaming apps.
- Microservices
Node.js is great for creating microservices and easy-to-use APIs. PayPal has used Node.js to power its microservices architecture since 2013.
Core Node.js Components
Node.js is built on a set of core components that together provide a robust, high-performance runtime for building scalable network applications. Understanding these Node.js components is essential for leveraging the framework to its full potential. This section explores the key elements that form the backbone of Node.js.
1. Event Loop
The event loop is the heart of Node.js, responsible for managing and executing asynchronous operations. Unlike traditional server-side environments that create a new thread for each client request, Node.js operates on a single-threaded event loop, which efficiently handles multiple client requests concurrently.
-
How It Works: The event loop continuously checks the event queue and processes callbacks from completed asynchronous operations. This non-blocking mechanism allows Node.js to handle thousands of connections simultaneously. This makes it ideal for I/O-heavy applications.
-
Phases of the Event Loop: The event loop consists of multiple phases, including timers, I/O callbacks, idle, prepare, poll, check, and close callbacks. We’ll talk about each of them in detail in the next section. Each phase has a specific purpose and processes different types of callbacks, ensuring efficient execution of tasks.
2. Node.js Process
The Node.js process is a global object that provides information about the current Node.js process. It is crucial for managing and controlling the execution of Node.js applications.
-
Process Object: The process object contains useful properties and methods, such as process.argv for command-line arguments, process.env for environment variables, and process.exit() to terminate the process.
-
Lifecycle: The lifecycle of a Node.js process includes initialization, execution of the script, handling of events, and termination. Understanding this lifecycle helps developers manage resources and optimize application performance.
3. Modules and Packages
Modules are building blocks of Node.js architecture and enable code organization and reuse. Node.js supports both CommonJS and ES6 modules and provides flexibility in how developers structure their code.
-
CommonJS Modules: CommonJS is the default module system in Node.js. Modules are created using module.exports and imported using require(). This system allows for encapsulation and separation of concerns.
-
ES6 Modules: ES6 modules are a standardized module system introduced in ECMAScript 2015. They use export and import statements and offer better integration with modern JavaScript tooling and frameworks.
-
Node Package Manager (NPM): NPM is the world’s largest software registry. It provides access to over 1.5 million packages and simplifies the management of dependencies, versioning, and distribution of reusable code.
4. Callbacks, Promises, and Async/Await
Asynchronous programming is a core concept in Node.js as it enables non-blocking operations. Node.js provides several mechanisms to handle asynchronous code, each with its own advantages and use cases.
-
Callbacks: Callbacks are functions passed as arguments to asynchronous operations, invoked when the operation completes. While straightforward, callback nesting (callback hell) can lead to complex and hard-to-read code.
-
Promises: Promises offer a more elegant way to handle asynchronous operations by representing the eventual completion or failure of an asynchronous task. They provide methods like then(), catch(), and finally() to handle outcomes.
-
Async/Await: Introduced in ECMAScript 2017, async/await is syntactic sugar built on promises, allowing developers to write asynchronous code that looks synchronous. It simplifies error handling and makes code more readable.
5. Node.js APIs
Node.js provides a rich set of APIs to facilitate the development of server-side applications. These APIs cover various functionalities, from file system operations to networking.
-
File System (fs) Module: The fs module provides methods for interacting with the file system, such as reading, writing, and deleting files. It supports both synchronous and asynchronous operations.
-
HTTP Module: The http module enables the creation of HTTP servers and clients. It provides methods to handle requests, responses, and various HTTP operations. It forms the foundation for building web applications.
-
Streams: Streams are an abstract interface for working with streaming data. Node.js stream API allows reading and writing data in chunks, which makes it efficient for handling large files and data flows.
-
Buffer: The Buffer class is designed for handling binary data. It provides methods to manipulate raw binary data directly, essential for working with TCP streams, file I/O, and other binary protocols.
Node.js Architecture
Software architecture is defined as the software infrastructure within which application components providing user functionality can be specified, deployed, and executed.
What kind of architecture does Node.js support? Node.js leverages the “Single Threaded Event Loop” architecture to take care of multiple concurrent clients.
The event loop allows Node.js to perform non-blocking I/O operations by offloading operations to the system kernel. Kernels are multi-threaded which means they can handle multiple operations executing in the background. When one of the operations completes, the kernel tells Node.js so that the appropriate callback may be added to the poll queue to be executed.
When Node.js starts, it initializes the event loop, processes the provided input script, then begins processing the event loop. Each phase has a FIFO queue of callbacks to execute. When the queue has been exhausted or the callback limit is reached, the event loop will move to the next phase, and so on.
Phases of the event loop include:
- timers: this phase executes callbacks scheduled by setTimeout() and setInterval().
- pending callbacks: executes I/O callbacks deferred to the next loop iteration.
- idle, prepare: only used internally.
- poll: retrieve new I/O events; execute I/O related callbacks (almost all with the exception of close callbacks, the ones scheduled by timers, and setImmediate()); node will block here when appropriate.
- check: setImmediate() callbacks are invoked here.
- close callbacks: some close callbacks, e.g. socket.on(‘close’, …).
Between each run of the event loop, Node.js checks if it is waiting for any asynchronous I/O or timers.
Node.js is an event-based platform which means that everything that happens in Node.js is the reaction to an event. The event loop is called the heart of Node.js. It indefinitely receives requests & processes them, and then returns the responses to corresponding clients.
Advantages of Using Node.js In Your Project
Big companies like LinkedIn, Uber, and even NASA adopted Node.js. Why? Because the benefits of NodeJS are unmatched.
- Easy Scalability
One of the major reasons why developers and businesses are adopting Node.js is because of its benefit of scaling. Scalability gives your application room to grow. Node’s scalability is achieved by the load balancing and the capability to handle a huge number of concurrent connections.
- Reduced Costs
With Node.js, the same programming language can be used on both the frontend & backend. It can save a lot of time and costs of recruiting several developers. If you’re looking for Node.js developers, LITSLINK is a software development hub that is ready to provide you with top experts.
- Fast-to-market Development
Node.js has an extensive package management library, with thousands of open-source options that can be added to your app project immediately which can reduce your time to market and programming budget.
- Handles the Requests Simultaneously
The system can effectively handle concurrent requests. The incoming requests get lined up and are executed quickly and systematically.
- Efficient Caching
Node.js has a powerful ability to cache data. Data can be retrieved quickly without the need to repeatedly query a database or perform time-consuming computations. This is often achieved using in-memory data stores such as Redis or Memcached.
- Big Community
An active community means a lot of support and feedback. Node.js is blessed to have a large community of programmers who keep on contributing towards its further improvement. Also, there are several community forums for Node.js such as Reddit, Nodebb, Dev.to, Github, and Stackoverflow.
- Node.js Also Inherited the Main JS Advantages
Node.js offers fast performance and data processing; highly reusable code; the code is easy to learn, write, read, and maintain; huge resource library.
Now as one of the most demanded frameworks in the world, Node.js helps developers create highly scalable and cutting-edge applications. But will it be the same popular in the future? Thought leaders say yes! Learn more about the future of Node.js in our blog.
Wrapping up
Node.js has become incredibly popular for both web and mobile application development. It is great for building apps with heavy client-side rendering and frequent shuffling of data from a client to a server.
The knowledge of the technology and its architecture is fundamental when it comes to software development. If you don’t want to waste your time and resources, you can rely on a professional team of developers. Our Node.js experts can answer all your questions.