The tech industry is a battlefield of brilliant ideas. Every day, countless software products jostle for user attention and market dominance. Yet, a staggering 70% of digital transformation projects fail, according to McKinsey. This begs the question: why do so many promising ventures fall short?
Often, the culprit lies in team structure. Building the wrong software development team structure is akin to navigating a storm with a leaky boat. Miscommunication, unclear roles, and a lack of synergy can sink even the most innovative projects.
This guide equips you with the tools to navigate the “software development abyss” by constructing a powerful software team structure. We’ll decipher the code behind common abbreviations like BA, PO, QA, and PM, and unveil the key approaches to building a dream team that weathers the storm and delivers exceptional results.
Here, you’ll discover:
- The critical ingredients of a high-performing software development team structure.
- Different team structure models to fit your project’s needs.
- Strategies for fostering effective communication and collaboration.
- How to identify and address common team challenges.
By the end of this guide, you’ll be empowered to assemble a software development team that not only survives the turbulent seas of product development but also thrives, transforming your next groundbreaking idea into a reality.
Agile Software Development: Communication Is a Priority
Agile software development is a methodology, the principal goal of which is to bring meaningful results through cooperation within a flexible team without a strong hierarchy. This methodology enables clients to get their products much faster and with fewer headaches.

While the traditional approach involves clearly defined roles among specialists and big software development teams, the Agile methodology is all about smaller teams without a strong hierarchical structure. With constant communication between a client and a software development team, specialists can adapt to various requirements and resolve issues within a team as they have the authority to suggest changes and make decisions.
|
Agile Team |
Traditional Team |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Choose the Agile software development team structure if:
- You need to spend less time on documentation
- You want to avoid micromanagement and provide your employees with more freedom during the development lifecycle
- It’s vital to launch your product as fast as possible
- Your solution requires many upgrades to work smoothly
- It’s crucial for you to be flexible with project planning
- You are ready to communicate with your team regularly.
Select a Software Team Structure to Suit Your Project
The Agile methodology requires constant communication between specialists so you will need a special type of team. It’s crucial to ensure every team member is aware of their colleagues’ tasks to help each other or swap tasks efficiently.
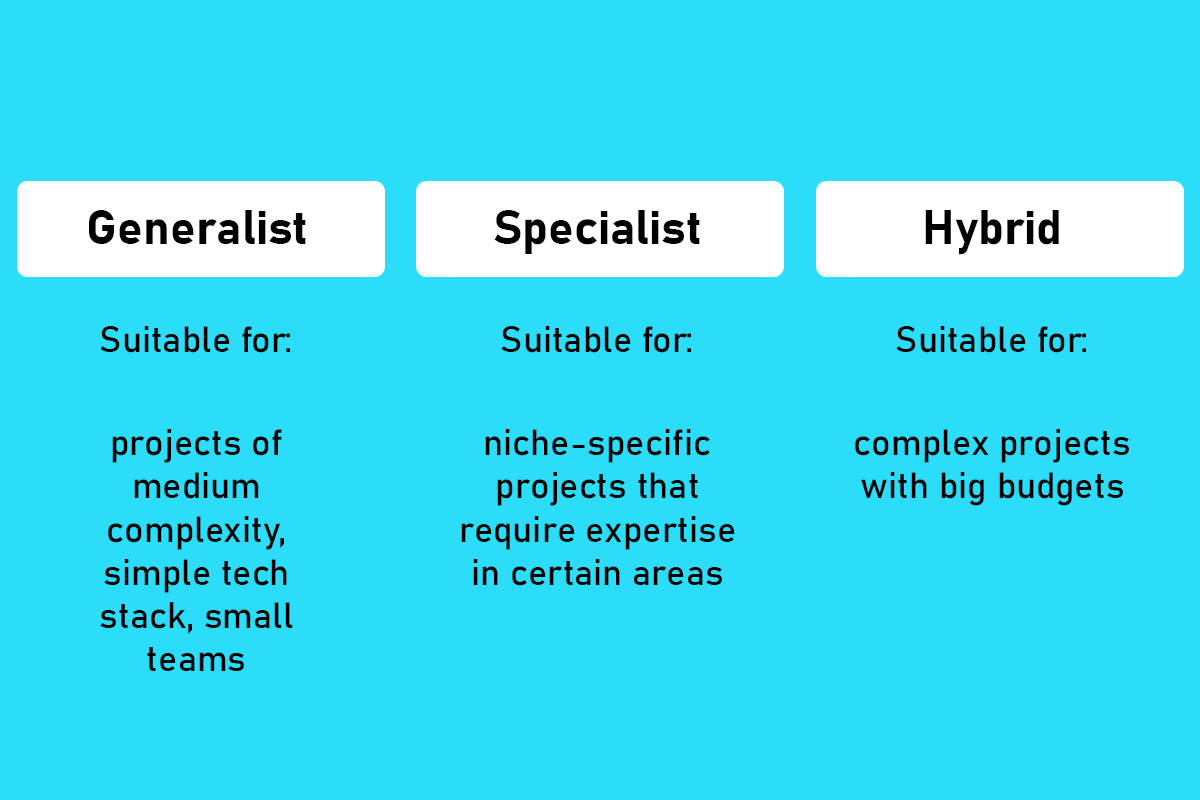
Depending on a certain type of software development team you need to build, there are three core approaches you have to consider when searching for the perfect employees: generalist, specialist, or hybrid.
-
Generalists
Suitable for: projects of medium complexity, simple tech stack, and small software development teams
This approach is a perfect match for you if you prefer to cooperate with a small software team and don’t want to equip your product with numerous complex features.
Multitasking, exchanging tasks, and performing multiple roles, your specialists will become universal soldiers to ensure you hit the market with a profitable solution as fast as possible. For instance, one of your designers can be familiar with quality assurance and test your software product as well.
Such software development teams usually include specialists with extensive skill sets and expertise. However, if you require your team members to be experts in a specific area, generalists may lack the knowledge you need to deliver a relevant solution.
But if you are limited in resources and want to opt for this approach, consider hiring a third-party contractor to perform niche-specific tasks.
-
Specialists
Suitable for: niche-specific projects of higher complexity that require expertise in a certain area
If you have in mind a complex project that requires deep expertise, consider applying this approach to get better results. Specialists are seasoned experts in particular programming languages or technologies and they don’t exchange tasks with their colleagues. Such a software team structure is perfect for building feature-rich and effective products much faster.
Since every team member works individually, specialists might face communication issues, so it’s crucial to equip your team with an experienced project manager to eliminate any obstacles along the way.
-
Hybrid Team
Suitable for: complex projects with big budgets
This approach involves both generalists and specialists and is suitable if you require both flexibility and deep expertise. Remember that a hybrid team is a costly endeavor as you will need lots of resources to connect your tech talents.
A hybrid software development team structure can be an amazing option for big projects—specialists will perform tasks that require deep expertise and develop separate components, while generalists will ensure the system is integrated.
Though the development lifecycle is more effective with hybrid teams, it might be tough to connect specialists with different approaches to the workflow. These software development teams need a seasoned PM to provide a client with a sophisticated product as fast as possible.
Assemble Your Powerful Team: The Key Roles and Responsibilities
A typical Agile software development team consists of:
-
Product Owner (PO)
This decision-maker represents both business stakeholders and end-users. They understand customer requirements and know how the product’s final version should function.
In order to effectively maximize the value of a product, the Agile product owner is involved in a variety of functions, including business strategy, product design, market analysis, and aspects of project management. Their job is to maintain a product backlog, balance trends, and business objectives, define the product roadmap, and communicate with a client to ensure a team gets valuable and relevant feedback.
-
Business Analyst (BA)
The main task of this team member is to process customer business goals and transform them into specific requirements. This person aligns the business model with technology to ensure a client gets a product that brings value to their audience.
Being a reliable mediator between a customer and a team, BA defines the market demands and comes up with the most suitable and profitable direction for business development.
-
Project Manager (PM)
A project manager is a process guru coordinating a software development team, communicating with a client, and eliminating any possible obstacles. They prioritize and distribute tasks among specialists, maintain project documentation, and organize business calls.
Whether a team has communication issues or a project goes over budget, a PM has to develop an action plan to eliminate the possible risks.

-
Software Architect
If you want to hit the market with a complex and scalable product, you will need a software architect to decide how integrations should work, perform code reviews, select the right technology stack, and make high-level design choices.
With an understanding of software architectural patterns and exceptional programming skills, this engineer aligns your requirements and users’ needs with the technical aspect of your solution.
-
Software Developer
A team of developers builds top-quality products and resolves any technical issues they face during the development lifecycle. A powerful team usually consists of front-end and back-end engineers. You can also hire full-stack developers with skills in various coding niches.
Front-end engineers work with customer-facing elements of your product: developing the user interface, creating cross-device responsive pages, and optimizing a product for maximum speed.
Back-end developers are responsible for your product’s functionality. From building and managing databases to integrating third-party APIs, these specialists deal with server-side programming to ensure your software product works without glitches.

-
UX/UI Designer
Designers’ task is to come up with the way end-users will interact with your product. These specialists build user journeys for flawless UX and create such elements as navigation buttons.
Leveraging UX designer services enables your end-users to interact with your solution consistently and intuitively. With user behavior in mind, this person creates prototypes for your product, conducts usability testing, and collaborates with a team of developers to build a feature-rich and profitable product.
A UI designer creates an easy-to-navigate interface for your product. Whether it’s a color scheme and logo of your solution or navigational elements like a search field and icons, this specialist makes your product’s interface straightforward and efficient.
-
Quality Assurance Engineer (QA)
This person detects any bugs before they get to end-users and ensures your product works without any issues. From performance and functionality to usability and security, QA engineers use numerous test environments to look for errors. Then, they report them to a team of developers so they can fix them as fast as possible.
Essential Tips on Keeping a Software Development Team Effective
-
Define the team size
Depending on your budget, business goals, and deadlines, the size of your team affects most aspects of the entire software development lifecycle. The optimal Agile team size is between four and nine specialists. If you need to opt for a traditional approach, you can collaborate with bigger teams.
Remember that smaller software teams are more flexible and can work independently. If you want to build a bigger team and keep it effective, split it into smaller groups to avoid management problems. You can divide your team into groups by development stages, roles, and specializations.
-
Make roles and responsibilities clear
When your software team has a common goal and every specialist is aware of their responsibilities, it’s much easier to stay productive and deliver meaningful results. Define areas of responsibility from the start to ensure all tasks are completed according to the agreed timeframes and budget.
-
Make your workplace friendly
A positive working environment is vital to keep specialists motivated and boost overall productivity. Make sure all issues are addressed and everybody can speak up and share their ideas with colleagues. If you have a strong hierarchical structure, reduce the power distance and allow specialists to take ownership in the workplace.
-
Ensure your team members can communicate efficiently
You can’t build a top-notch product without a stress-free communication model. Don’t forget to provide your team with all the essential tools for transparent communication. You can use such business messaging apps as Chanty, Slack, and Zoho Cliq.
Video conferencing software like Zoom and Webex Meetings will help your team stay on track to meet crucial goals and enhance communication quality.
-
Avoid micromanaging your software team
Micromanagement annoys specialists, damages their trust, and can cause burnout. You can start by talking to your tech talents to establish trust and prioritizing the tasks that are vital for you to stay involved in.
Project management tools can be a fantastic way to provide your team members with the space they need and delegate tasks properly. Tools like Airtable, Trello, and ClickUp will help you manage tasks, create custom reports, and collaborate in real time.
How to Scale Agile Teams
As your project grows and complexity increases, you might need to scale your Agile team. Here are some effective strategies:
- LeSS (Large-Scale Scrum): LeSS extends the principles of Scrum to larger teams. It advocates for a single Product Backlog, shared across all teams, promoting transparency and collaboration. LeSS emphasizes simplifying organizational structures to enable seamless coordination among multiple teams.
- SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework): SAFe provides a comprehensive approach to scaling Agile, incorporating principles from Lean and DevOps. It offers roles, ceremonies, and artifacts tailored for large enterprises. SAFe introduces constructs like Agile Release Trains (ARTs) to synchronize delivery across multiple teams, fostering alignment and reducing dependencies.
- Nexus Framework: Nexus is a scaling framework specifically designed for Scrum. It provides guidance on organizing multiple Scrum teams to deliver a single product. Nexus introduces additional events, such as the Nexus Sprint Planning and Nexus Sprint Review, to facilitate integration and coordination among teams.
- Evolving Architecture: As teams scale, maintaining a coherent architecture becomes crucial. Implementing practices like Domain-Driven Design (DDD) or Event Storming can help teams manage complexity by defining clear boundaries between different parts of the system. This enables teams to work independently while ensuring compatibility and integration.
- Continuous Integration and Delivery (CI/CD): Automating the build, test, and deployment processes streamlines the integration of code changes from multiple teams. CI/CD pipelines enable frequent and reliable releases, reducing the risk associated with integrating changes from disparate sources.
- Distributed Agile Teams: With the rise of remote work, distributed Agile teams are increasingly common. Leveraging tools for communication, collaboration, and project management becomes essential for maintaining cohesion and transparency across geographically dispersed teams.
- Agile Coaching and Mentoring: Investing in Agile coaches and mentors can facilitate the scaling process. Coaches provide guidance on Agile principles, practices, and mindset, helping teams overcome challenges associated with scaling. They also promote a culture of continuous improvement, fostering resilience and adaptability within the organization.
- Metrics and Feedback Loops: Establishing meaningful metrics and feedback loops enables teams to assess their performance and identify areas for improvement. Metrics like lead time, cycle time, and velocity provide insights into team productivity and predictability, guiding decision-making at scale.
- Communities of Practice (CoPs): Encouraging the formation of communities of practice allows teams to share knowledge, experiences, and best practices. These communities serve as forums for collaboration and learning, fostering a culture of innovation and cross-pollination of ideas across the organization.
Overall, with the adoption of these advanced strategies, organizations can effectively scale Agile teams to tackle complex projects and deliver value with speed and efficiency.
How to Choose the Right Team Structure
Choosing the right team structure is a critical decision that can significantly impact the success of a project. Here are additional factors and considerations to guide your decision-making process.
Technical requirements
The nature of the project’s technical requirements plays a significant role in determining the appropriate software development team structure. Projects that involve cutting-edge technologies or highly specialized domains may benefit from dedicated teams with expertise in those areas. Conversely, projects with more straightforward technical requirements may be suitable for generalist teams.
Market dynamics
Understanding the market dynamics and competitive landscape can inform the selection of the software development team structure. In fast-paced industries where innovation is key, teams need to be nimble and adaptable. This might favor smaller, Agile teams that can quickly respond to changing market demands. Conversely, in industries with stable market conditions, larger, more structured teams might be appropriate.
Regulatory and compliance requirements
Projects subject to stringent regulatory or compliance requirements may require specialized teams with expertise in navigating regulatory frameworks. These teams must ensure that the project adheres to all relevant regulations and standards, which may necessitate additional roles or expertise within the team structure.
Risk management
Assessing and managing risks inherent in the project is crucial in determining the software development team structure. High-risk projects may benefit from specialized risk management teams or dedicated roles focused on risk mitigation strategies. Conversely, low-risk projects may prioritize flexibility and efficiency, favoring smaller, cross-functional teams.
Stakeholder expectations
Understanding the expectations and preferences of key stakeholders is essential in shaping the software development team structure. Stakeholders may have specific requirements regarding communication channels, reporting structures, and team composition. Aligning the team structure with stakeholder expectations fosters transparency, collaboration, and ultimately, project success.
Geographical considerations
In an increasingly globalized world, the geographical distribution of team members can influence the team structure. Distributed teams may face unique challenges related to communication, collaboration, and time zone differences. Selecting a software development team structure that accommodates the geographical distribution of team members is critical for maintaining productivity and cohesion.
Organizational structure
The existing organizational structure and hierarchy within the company can impact the selection of the software development team structure. Projects operating within a matrix organizational structure may have access to a diverse pool of resources but may also face challenges related to conflicting priorities and reporting lines. Aligning the team structure with the broader organizational context ensures synergy and coherence across different projects and departments.
Effective Team Leadership
Effective team leadership is indispensable for driving a development team toward success, irrespective of the chosen structure. A proficient leader exhibits several key qualities that inspire and empower team members:
- Clear communication skills. Strong leaders excel in articulating project objectives, expectations, and impediments to the team in a transparent and concise manner. They foster open communication channels, ensuring that everyone is on the same page regarding project goals and progress. According to the State of Business Communication survey, the primary advantages of effective communication include heightened productivity (72%), enhanced customer satisfaction (63%), and boosted employee confidence (60%).
- Technical proficiency. A leader with a solid grasp of software development processes and technologies can provide valuable guidance and direction to the team. Their technical expertise enables them to make informed decisions, offer practical solutions, and provide mentorship to team members when faced with technical challenges.
- Effective problem-solving abilities. Leaders adept in problem-solving possess the agility and resourcefulness to identify and address obstacles encountered during the development lifecycle. They encourage a proactive approach to problem-solving within the team, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
- Motivation and delegation. Motivating team members and delegating tasks efficiently are hallmark traits of effective leaders. They recognize individual strengths and talents within the team, align tasks with team members’ skills and interests, and provide ample opportunities for professional growth and development. By fostering a positive work environment characterized by trust, collaboration, and empowerment, leaders cultivate a motivated and high-performing team.
Adaptability and resilience. In a dynamic and rapidly evolving environment, adaptive leadership is essential. Effective leaders demonstrate resilience in the face of challenges, adapting their approach as needed to overcome obstacles and achieve project objectives. They remain flexible and responsive to change, guiding the team through uncertainty with confidence and composure.
Find a Perfect Software Team for Your Project With LITSLINK
Using the Agile methodology, our software development agency provides clients worldwide with valuable results. Whether you need a group of experienced specialists or a team of flexible generalists, LITSLINK is here to help!
With a vast pool of seasoned engineers, designers, QA specialists, and project managers, we are ready to skyrocket your business!