Every business starts with a plan. Google began in a garage as a scrappy, bootstrap-funded venture, while Airbnb’s founders launched their business simply to make a few extra bucks. Let’s not forget that even the world’s biggest companies started with a plan.
To execute this plan successfully, startups need a powerful tool: the Lean Canvas, a modernized version of the traditional business model canvas. This framework helps transform bold ideas into tangible products, validate market fit, and scale effectively.
In this article, we explore what Lean Canvas is and how examples of its use can be leveraged to enhance your business.
What Does the Lean Canvas Model Entail?
The lean canvas model serves as a concise business model template crafted to assist entrepreneurs and innovators in dissecting their ideas and pinpointing crucial assumptions. Aligned with the principles of the Lean Startup methodology, this tool follows an agile and iterative approach, emphasizing the “build-measure-learn” philosophy.
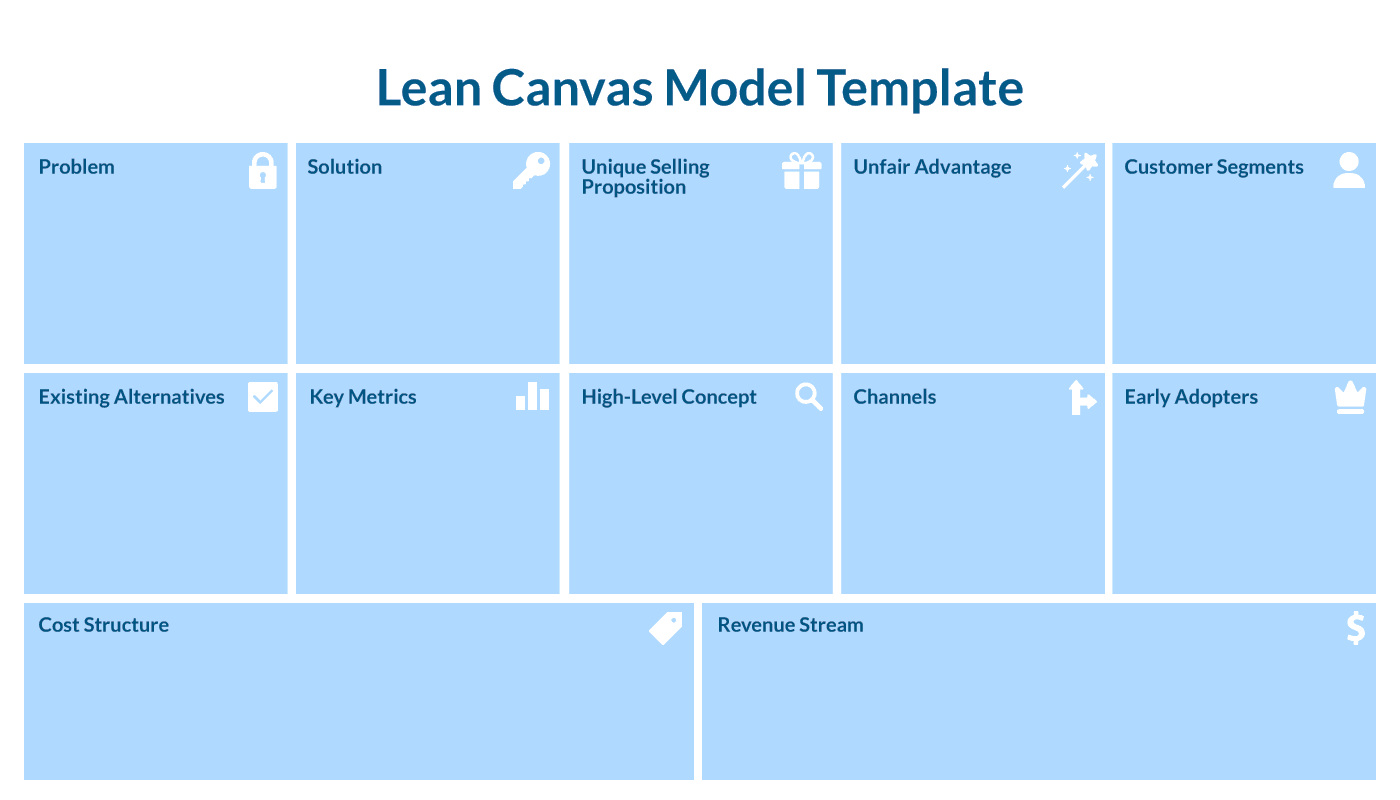
What’s the main goal?
Consider it a visual roadmap that directs attention to the fundamental aspects of your business, prompting a focus on solving customer problems sustainably. Derived from the more extensive business model canvas, the lean canvas model adopts a leaner and action-oriented stance, emphasizing nine pivotal building blocks crucial for validating ideas and achieving product-market fit:
- Customer Segments: Identifying the target audience for your product or service.
- Problem: Addressing specific pain points for your target customers.
- Solution: Outlining how your product or service resolves the identified problem.
- Value Propositions: Highlighting unique benefits compared to competitors.
- Unfair Advantage: Establishing what makes your business sustainable and defensible.
- Channels: Determining how you will reach your target customers and deliver your value proposition.
- Revenue Streams: Defining how you will generate income from your customers.
- Cost Structure: Identifying key expenses associated with running your business.
- Key Metrics: Establishing how you will measure the success of your business.
Completion of these sections provides a comprehensive understanding of your business model, revealing potential strengths and weaknesses. The one-page format encourages focus and prioritization, steering clear of unnecessary details.
Lean Canvas or Business Model Canvas?
Every startup starts with a winning idea and strategy. A well-planned business strategy is what all entrepreneurs should have to jumpstart their ventures, stay ahead of market competition, and generate revenue. The universal golden standard doesn’t exist either for enterprises or startups. Thus, experimentation and the ability to learn from mistakes are the core skills of every young company.
Both business and lean canvas models use the above-mentioned tactics.
If you are about to start your own business and doubt which tool will make the best match for you, we outline the core differences between the two models.
- Model orientation.
The lean canvas model focuses on finding surefire solutions to marketing problems through learning from mistakes. Instead, the business canvas model is designed for all companies aiming at verifying marketing hypotheses on the market.
- Marketing Approaches
The business model canvas focuses on customer segmentation and aims to explore how to build trustworthy relationships with clients. Conversely, the lean canvas model applies a different approach. It’d rather focus on testing a product idea.
- Unique Value Proposition
All entrepreneurs, whether they are experienced startuppers or they’ve just founded their first company, strive to deliver value to customers. They find it by making many mistakes and testing various ideas with different audiences. The business model canvas doesn’t join this bumpy road. Business executives know about their product value and seek to find effective communication channels to reach their customers.
If you’re curious to find out how a unique value proposition is created, have a look at IT outsourcing case studies built by LITSLINK’s seasoned software engineers.
Exploring 13 Lean Canvas Models Through Giant Company Examples

Not so many startups are lucky enough to be on the rise. Most of them do fail. The main problem is that they lack successful product ideas, which could capture the clients’ attention. The lack of market research, poor understanding of the customers’ needs, and inability to customize the product are just a few of the reasons why most startups fail. In this case, the lean canvas model might help startups spot inefficiencies, predict risks, and highlight their strong points.
Since the best way to learn is to learn from other’s mistakes and achievements, in this article, we decided to look at 5 lean canvas examples and discover how they paved
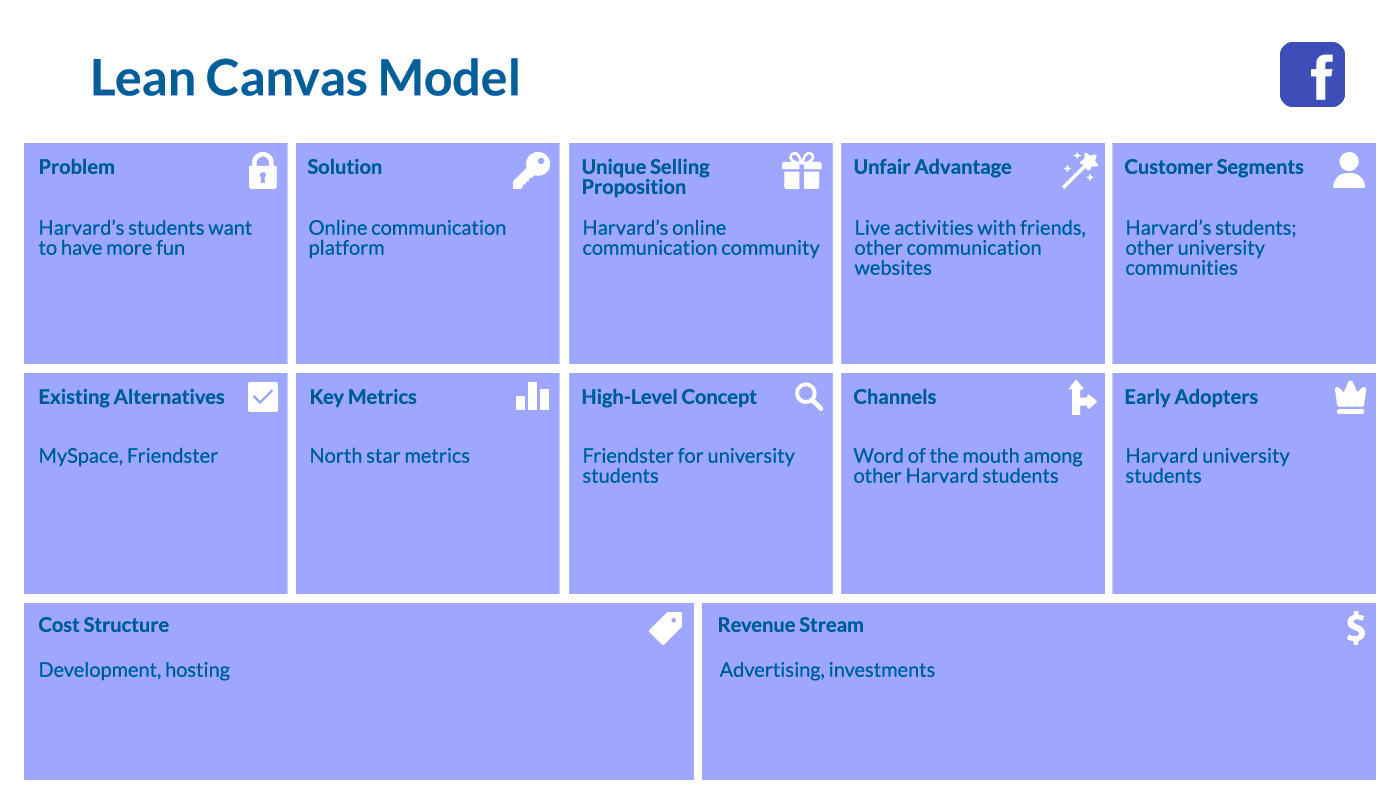
1. Facebook
Founded: 2004
Created by: Mark Zuckerberg
Country: USA, Cambridge, Massachusetts.
Total Funding: $104 billion (Valuation at IPO)
The story of creating this famous social media network started in the dormitory of Harvard University. Mark Zuckerberg, a sophomore student at that time, was working on a product that would allow students to share visual content with their friends online.
As Facebook’s founder explained in one of his interviews he just wanted to solve the students’ problem – have a common place for online communication. Despite many useless efforts, Mark Zuckerberg nailed it!
If we could apply the lean canvas model example to Facebook, it would look like this at the outset of the startup’s journey:
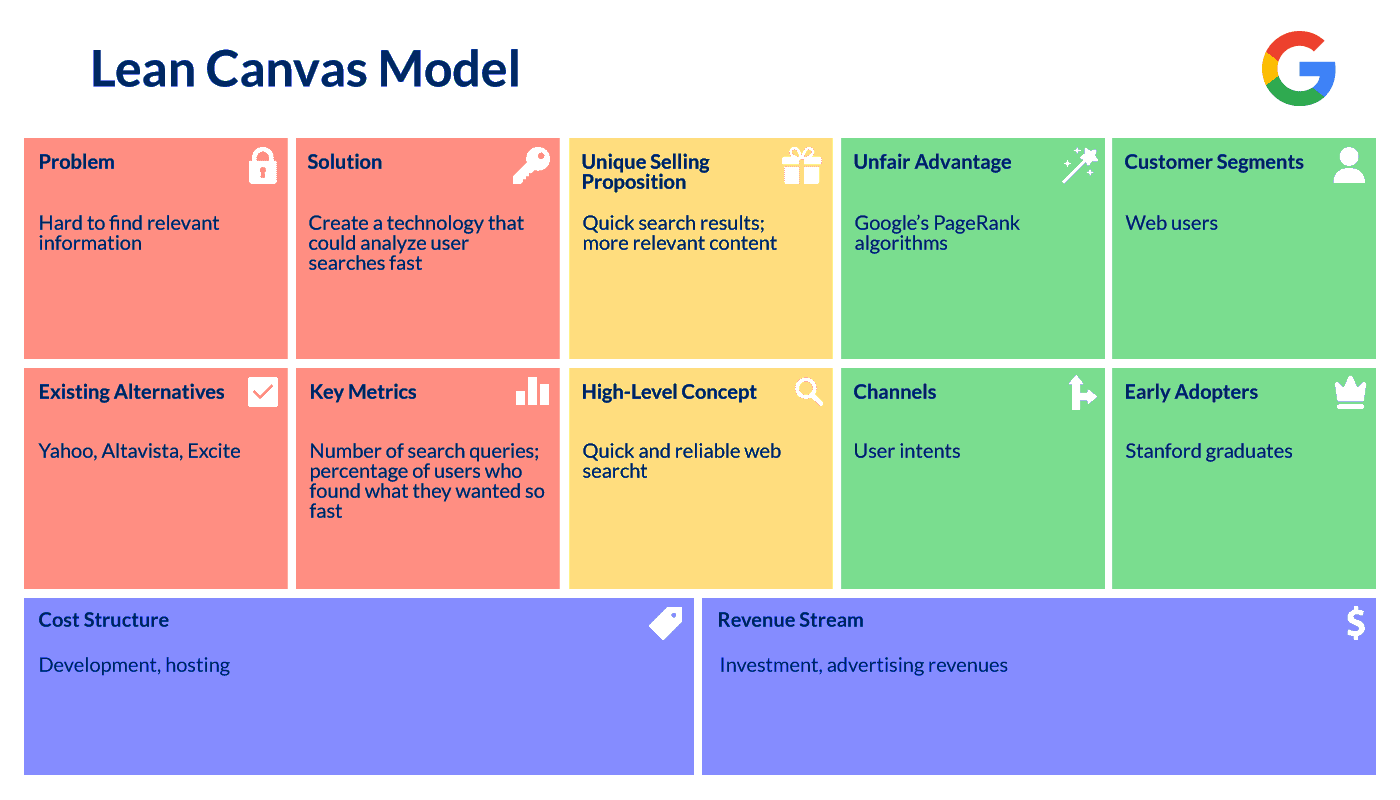
2. Google
Founded: 1998
Created by: Sergey Brin & Larry Page
Country: USA, Menlo Park, California
Total Funding: $23.1 billion (Valuation at IPO)
Not only Harvard students could generate innovative ideas, but Stanford University enthusiasts jumped on this bandwagon as well. Larry Page and Sergey Brin were two graduates from the computer science faculty, who created a PageRank algorithm for a newly developed search engine–BackRub, which was the first name of Google. With the help of this technology, users can find relevant content at a high speed. It was the main competitive advantage of Page and Larry’s product over other popular search engines like Yahoo and Excite.
How could Google use the lean canvas model template during the initial startup development phase? Let’s have a look at the chart below:
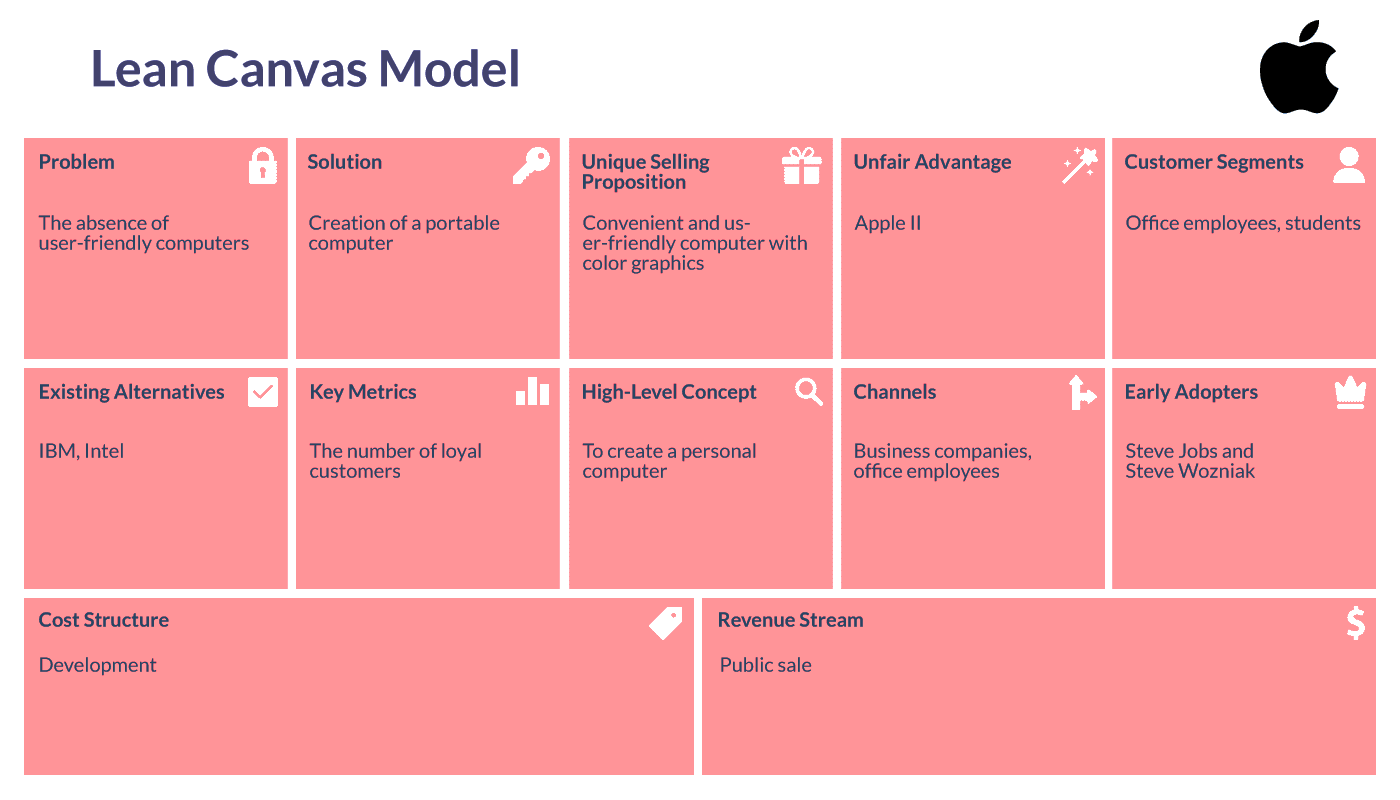
3. Apple
Founded: 1976
Created by: Steve Jobs & Steve Wozniak
Country: USA, Cupertino, California
Total Funding: $6,2 billion
Portable and user-friendly computers didn’t exist in the 1970s. This idea came to the minds of Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak in 1976. At that time, they made an important decision to leave college and establish the company they were so passionate about. Changing the way people use computers was the idea that inspired them to reach new heights. Working in Steve Jobs’ garage, they created Apple I, and then – Apple II, which intended to revolutionize the industry with color graphics.
Almost several years thereafter, Apple Inc. became one of the most profitable companies on the US market.
So, let’s review how could Apple use the lean canvas example at the very beginning of its success journey:
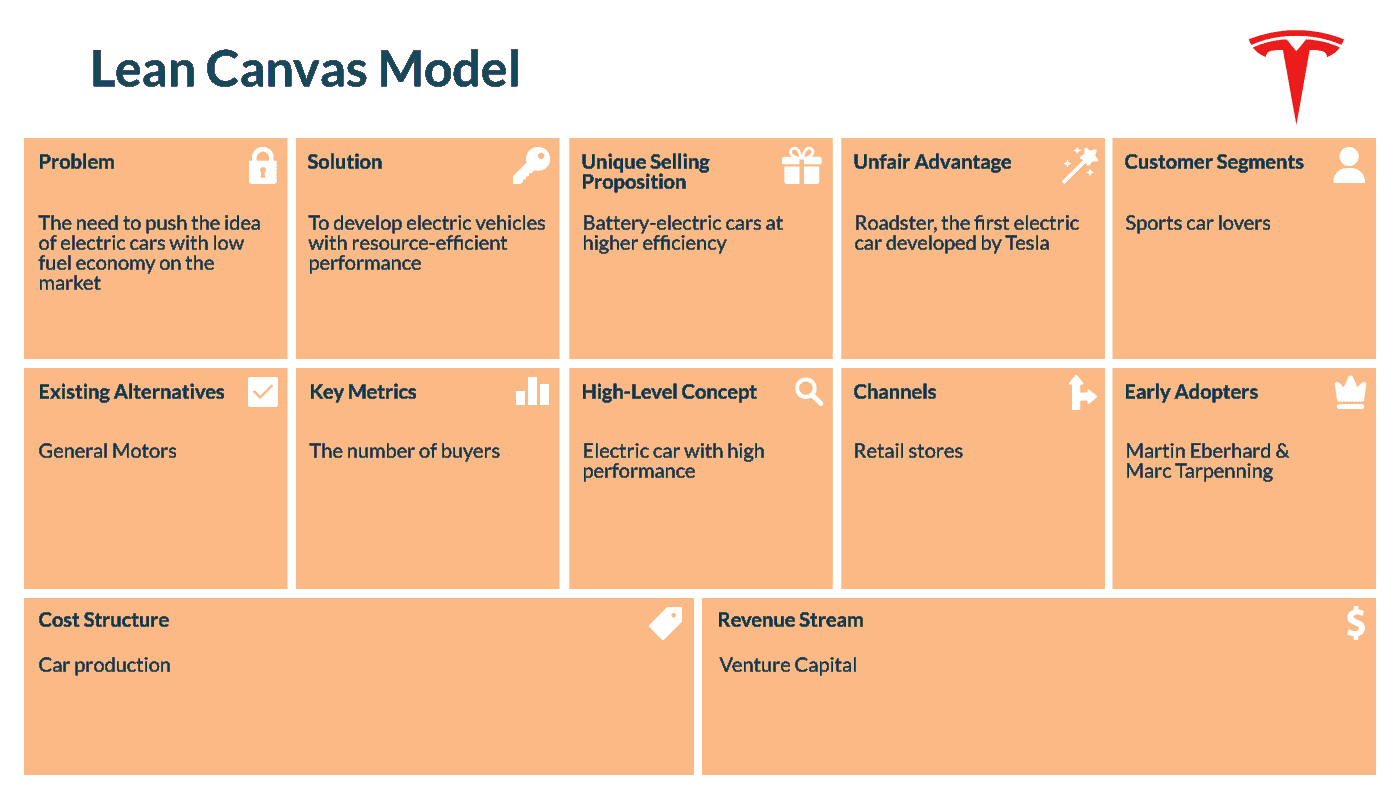
4. Tesla
Founded: 2003
Created by: Martin Eberhard & Marc Tarpenning
Country: USA
Total Funding: $19.9 billion
The two US entrepreneurs, Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning, picked up the idea of inventing electric cars in 2003 when an automotive giant – General Motors – failed with its electric vehicle – EV1.
The foundation story of Tesla doesn’t resemble the startup path of Google, Facebook, and Apple. The newly emerged company, named on behalf of a famous Serbian inventor, Nikola Tesla, strived to push the idea of electric cars on the market. In 2004, Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning searched for venture capital funding and got in touch with Elon Musk, PayPal’s co-founder. He invested $6,5 million in the first investment round and joined the board of directors at Tesla.
Let’s imagine that Tesla decided to use the lean business canvas model template. So, how will it look? Below, there is a graph, showing Tesla’s jumpstart:
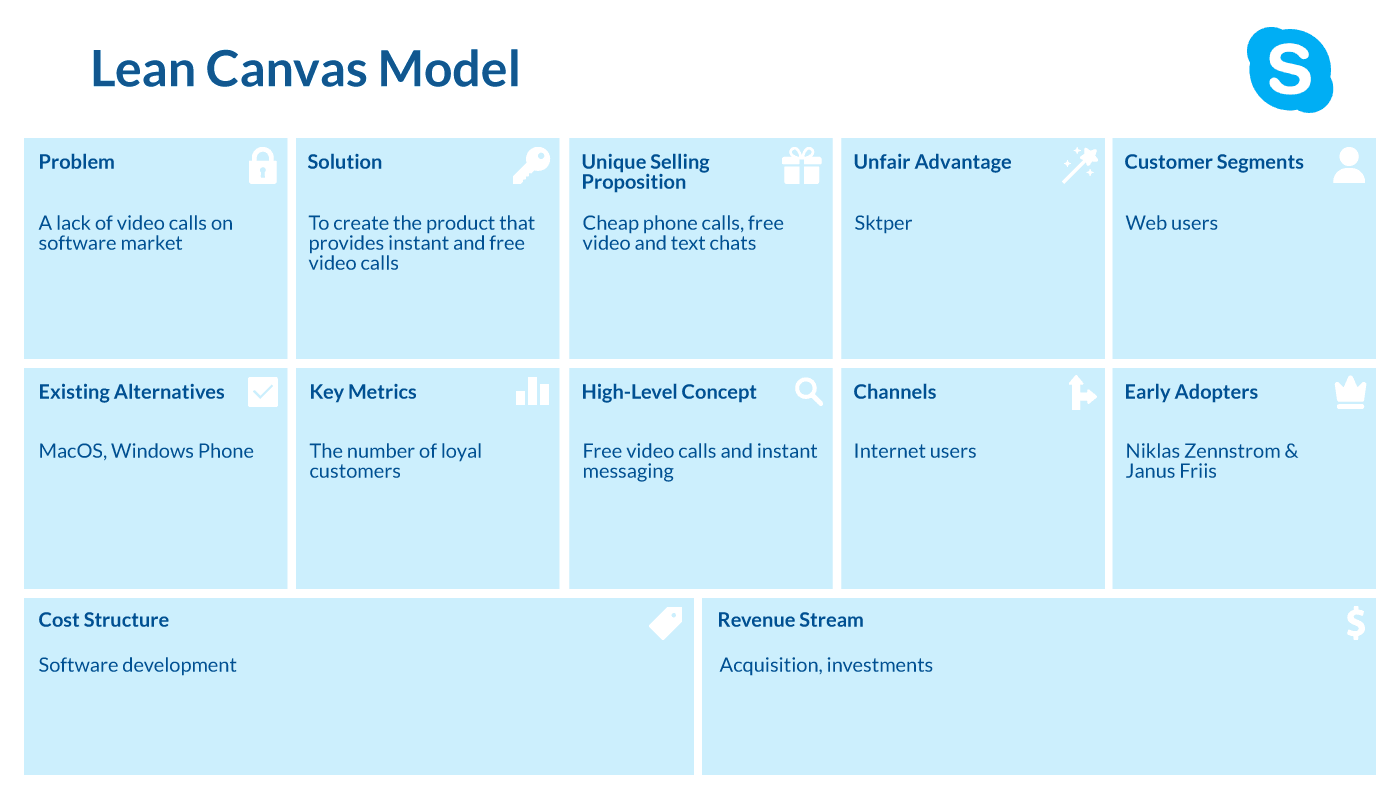
5. Skype
Founded: 2003
Created by: Niklas Zennstrom & Janus Friis (founders)
Country: Estonia, Sweden
Total Funding: $76.8 million
Skype was founded by two entrepreneurs – Niklas Zennstrom and Janus Friis in 2003. Inspired by the idea of free Internet voice calls, new software became a mere nightmare for phone companies. Since wireless networks gathered momentum in the early 2000s, a traditional phone service could be replaced by products like Skype.
The product was created by Estonian developers Priit Kasesalu, Ahti Heinla, and Jaan Tallinn, who worked on Kazaa, a file-sharing app. The first versions of Skype were available on several operating systems like Linux, Windows, and MacOS.
How could the lean canvas model be incorporated into Skype? Take a closer look at the graph here.
6. Airbnb
Founded: 2008
Created by: Brian Chesky, Joe Gebbia, Nathan Blecharczyk
Country: United States
Total Funding: $6.4 billion
Airbnb was founded in 2008 by Brian Chesky, Joe Gebbia, and Nathan Blecharczyk. The idea came to life when Chesky and Gebbia rented out air mattresses in their apartment to attendees of a conference. This was a cheaper alternative to hotels. They quickly realized the potential for a platform to connect travelers with hosts and offer unique and affordable stays.
With trust as a cornerstone, Airbnb integrated features like verified profiles, reviews, and a secure payment system to build confidence among users. Today, it’s one of the most prominent players in the travel industry.
How could the lean canvas model be incorporated into Airbnb? Take a closer look at the table here.
| Problem | High accommodation costs and lack of personalized, unique lodging options for travelers. |
| Solution | A platform connecting hosts with guests for affordable and unique short-term stays. |
| Unique Selling Proposition | “Belong anywhere” — Affordable, local, and unique accommodations worldwide. |
| Unfair Advantage | Network effects from a growing user base, verified reviews, and secure payment processes. |
| Customer Segments | Budget-conscious travelers, adventurers, and business travelers seeking unique stays. |
| Existing Alternatives | Hotels, motels, hostels, and other vacation rental platforms. |
| Key Metrics | Number of bookings, customer retention rate, host-to-guest ratio, and revenue per booking. |
| High-Level Concept | “An eBay for short-term rentals” — A community-based marketplace for accommodations. |
| Channels | Online advertising, social media, referral programs, and partnerships with travel influencers. |
| Early Adopters | Tech-savvy travelers and event attendees looking for budget-friendly stays in urban areas. |
| Cost Structure | Platform development, marketing and advertising, payment processing, customer support. |
| Revenue Stream | Commission from bookings (charged to both guests and hosts). |
7. Dropbox
Founded: 2007
Created by: Drew Houston, Arash Ferdowsi
Country: United States
Total Funding: $1.7 billion
Dropbox was born from Drew Houston’s frustration with forgetting his USB drive. Founded in 2007 with Arash Ferdowsi, Dropbox offered seamless file synchronization and cloud storage to solve the problem of unreliable file-sharing methods.
The startup’s freemium model was pivotal to its growth and attracted millions of users by offering free storage with an upgrade option. This strategy generated widespread adoption and built a loyal customer base.
| Problem | File-sharing methods were cumbersome, unreliable, and lacked synchronization across devices. |
| Solution | A cloud-based platform enabling seamless file storage, sharing, and synchronization. |
| Unique Selling Proposition | “Your files, anywhere, anytime” — Reliable access to files across all devices with minimal effort. |
| Unfair Advantage | Proprietary technology for file synchronization and strong word-of-mouth marketing. |
| Customer Segments | Individual users, freelancers, students, and businesses needing reliable file storage solutions. |
| Existing Alternatives | USB drives, email attachments, and competing cloud services like Google Drive or Microsoft OneDrive. |
| Key Metrics | Number of active users, storage usage, conversion rate from free to paid plans, and customer retention. |
| High-Level Concept | “A virtual hard drive in the cloud” — Effortless and secure file storage for everyone. |
| Channels | Online advertising, freemium model, referral programs, and partnerships with device manufacturers. |
| Early Adopters | Tech-savvy individuals and professionals frustrated with traditional file-sharing methods. |
| Cost Structure | Cloud infrastructure, platform development, marketing, and customer support. |
| Revenue Stream | Subscription fees for premium plans offering additional storage and advanced features. |
8. Uber
Founded: 2009
Created by: Travis Kalanick, Garrett Camp
Country: United States
Total Funding: $25 billion
Uber was founded in 2009 by Travis Kalanick and Garrett Camp after Camp struggled to find a cab during a snowy evening in Paris. Their platform allowed users to book rides easily through a mobile app.
Uber disrupted the traditional taxi industry by offering affordable, reliable, and convenient ride-hailing services. Its dynamic pricing model ensured availability during peak hours, and its user-friendly app gained traction with tech-savvy urbanites.
Here’s a detailed Lean Canvas table for Uber:
| Problem | Difficulty in finding reliable, affordable, and convenient transportation options, especially in urban areas. |
| Solution | A mobile app that connects passengers with drivers of vehicles for hire, providing fast and reliable transportation. |
| Unique Selling Proposition | “The smartest way to get around” — Affordable, convenient, and quick rides at the touch of a button. |
| Unfair Advantage | Network effects, massive user base, advanced GPS and route optimization technology, and high driver-partner engagement. |
| Customer Segments | Urban commuters, tourists, business professionals, and individuals in need of quick transportation. |
| Existing Alternatives | Traditional taxis, public transportation, and other ride-hailing services like Lyft. |
| Key Metrics | Number of active users, number of rides per day, driver ratings, and revenue per ride. |
| High-Level Concept | “A personal driver in your pocket” — On-demand ride-hailing service for users and drivers. |
| Channels | Mobile app stores, referral programs, partnerships with businesses, digital marketing, and influencer collaborations. |
| Early Adopters | Tech-savvy individuals, urban dwellers, and travelers looking for a faster and more convenient way to get around. |
| Cost Structure | Driver compensation, platform development, marketing, insurance, and customer support. |
| Revenue Stream | Ride fare commission (from both passengers and drivers), surge pricing, and partnerships with businesses for corporate rides. |
9. Spotify
Founded: 2006
Created by: Daniel Ek, Martin Lorentzon
Country: Sweden
Total Funding: $2.06 billion
Spotify was founded in 2006 by Daniel Ek and Martin Lorentzon to address the rising issue of music piracy. They created a platform that offered legal, on-demand music streaming supported by advertisements and a premium subscription model.
Spotify’s partnerships with record labels ensured a vast music library, attracting users who sought convenience and variety. Its algorithm-driven recommendations further enhanced user engagement, making it a leader in the music streaming industry.
Here’s how the lean canvas model could be incorporated into Spotify.
| Problem | Music piracy and limited legal, convenient access to streaming music. |
| Solution | A music streaming service offering millions of tracks with a freemium model (free with ads, premium without). |
| Unique Selling Proposition | “Music for everyone” — Access to a vast music library with personalized recommendations and playlists. |
| Unfair Advantage | Proprietary algorithms for music recommendations and playlist curation, exclusive artist partnerships. |
| Customer Segments | Music lovers, casual listeners, artists, and people seeking convenient and legal ways to listen to music. |
| Existing Alternatives | Illegal downloads, iTunes, YouTube, and other music streaming platforms (Apple Music, Amazon Music). |
| Key Metrics | Number of active users, monthly listens, conversion rate from free to premium, and user engagement. |
| High-Level Concept | “A radio that knows you” — Personalized music streaming with a freemium model. |
| Channels | Digital marketing, influencer partnerships, social media, and exclusive artist content. |
| Early Adopters | Tech-savvy music enthusiasts and early adopters of streaming services. |
| Cost Structure | Licensing fees to record labels, platform development, marketing, and customer support. |
| Revenue Stream | Subscription fees for premium accounts, ad revenue from free users, and partnerships with brands for exclusive content. |
10. Zoom
Founded: 2011
Created by: Eric Yuan
Country: United States
Total Funding: $156 million
Eric Yuan founded Zoom in 2011. Driven by a vision to create a simple, reliable video communication tool, Yuan created one. His experience at Cisco WebEx revealed the need for a more user-friendly and stable solution.
Zoom’s success lies in its ease of use, high-quality video performance, and scalability for businesses of all sizes. Its freemium model and word-of-mouth marketing helped it rapidly gain users, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Here’s a compelling Lean Canvas table for Zoom:
| Problem | Difficulty in conducting reliable, easy-to-use video conferences, particularly for remote teams. |
| Solution | A user-friendly, high-quality video communication platform for meetings, webinars, and collaboration. |
| Unique Selling Proposition | “A simple, reliable video conferencing tool for everyone” — Seamless video meetings with high-quality performance. |
| Unfair Advantage | Superior video quality, ease of use, and scalability for large meetings, with strong brand recognition. |
| Customer Segments | Remote workers, businesses, educational institutions, and organizations needing virtual meeting solutions. |
| Existing Alternatives | Skype, Google Meet, Microsoft Teams, WebEx, and other video conferencing tools. |
| Key Metrics | Number of active users, meeting duration, conversion from free to paid plans, user satisfaction. |
| High-Level Concept | “The best video conferencing experience for businesses of all sizes” — Reliable, simple, and scalable video meetings. |
| Channels | Direct sales, word-of-mouth, freemium model, digital marketing, partnerships with enterprises. |
| Early Adopters | Businesses, educational institutions, and tech-savvy users seeking reliable video communication tools. |
| Cost Structure | Cloud infrastructure, platform development, marketing, customer support, and partnership management. |
| Revenue Stream | Subscription fees for premium features, enterprise-level accounts, and add-ons such as webinars. |
11. TikTok
Founded: 2016
Created by: Zhang Yiming
Country: China
Total Funding: $6.1 billion
TikTok was launched in 2016 by Zhang Yiming’s ByteDance. Initially, it was designed to fill a gap in short-form video content creation and sharing. It combines music, filters, and editing tools to empower users to create engaging, creative videos.
TikTok succeeded due to its advanced AI algorithm, which delivers highly personalized content. As a result, it’s one of the fastest-growing social media platforms globally, appealing to younger generations. Learn more about recommendation algorithms in our blog article about Netflix’s AI algorithms.
| Problem | Limited platforms for creating and sharing short-form video content, with most focusing on longer content. |
| Solution | A mobile-first platform for creating, sharing, and discovering short, engaging videos with music, effects, and filters. |
| Unique Selling Proposition | “Endless entertainment with short, creative videos” — Personalized, algorithm-driven content tailored to users’ interests. |
| Unfair Advantage | Advanced AI algorithms for hyper-targeted content delivery, rapid virality, and strong user engagement. |
| Customer Segments | Gen Z and Millennials, content creators, influencers, and advertisers. |
| Existing Alternatives | YouTube, Instagram Reels, Snapchat, Vine (historical), Facebook. |
| Key Metrics | Daily active users, video views, user engagement (likes, comments, shares), and content creation rates. |
| High-Level Concept | “The most addictive short-form video platform” — A creative space for self-expression and viral content. |
| Channels | Social media, influencer marketing, viral challenges, partnerships with musicians, and cross-platform sharing. |
| Early Adopters | Young, trend-conscious individuals, influencers, and brands looking to engage with viral content. |
| Cost Structure | Cloud infrastructure, content moderation, user acquisition, marketing, and influencer partnerships. |
| Revenue Stream | Advertising (in-feed ads, brand partnerships), sponsored content, and in-app purchases. |
12. Canva
Founded: 2012
Created by: Melanie Perkins, Cliff Obrecht, Cameron Adams
Country: Australia
Total Funding: $572 million
Melanie Perkins founded Canva in 2012 when saw a gap in accessible graphic design tools. Along with Cliff Obrecht and Cameron Adams, she launched a platform to help non-designers create professional visuals easily.
With its drag-and-drop interface and extensive template library, Canva democratized design for individuals, businesses, and educators. Its freemium model attracted users worldwide, fueling its rapid growth.
The lean canvas model can be incorporated into Canva in this way:
| Problem | Lack of accessible, user-friendly tools for non-designers to create professional-quality graphics. |
| Solution | An easy-to-use online graphic design tool with drag-and-drop features, templates, and resources. |
| Unique Selling Proposition | “Empowering everyone to design anything” — Professional-quality design made simple for all users, no design experience needed. |
| Unfair Advantage | A vast library of templates, photos, and fonts, combined with a user-friendly interface and strong community of users. |
| Customer Segments | Small businesses, marketers, bloggers, educators, students, and non-designers who need easy graphic design solutions. |
| Existing Alternatives | Adobe Photoshop, Microsoft PowerPoint, Microsoft Paint, and other graphic design tools. |
| Key Metrics | Number of active users, design frequency, templates used, and conversion rates from free to premium plans. |
| High-Level Concept | “An easy and powerful design tool for everyone” — A cloud-based design platform accessible to anyone. |
| Channels | Social media marketing, content marketing, influencer collaborations, email marketing, and referrals. |
| Early Adopters | Entrepreneurs, bloggers, educators, and small businesses need to create professional designs without hiring designers. |
| Cost Structure | Platform development, cloud infrastructure, licensing of design assets (photos, fonts), marketing, and customer support. |
| Revenue Stream | Subscription fees for premium features (Canva Pro), team subscriptions, and sale of design elements (photos, templates). |
13. Pinterest
Founded: 2010
Created by: Ben Silbermann, Paul Sciarra, Evan Sharp
Country: United States
Total Funding: $1.5 billion
In 2010, Ben Silbermann, Paul Sciarra, and Evan Sharp launced Pinterest as a visual discovery platform. Users could pin ideas, images, and inspiration onto virtual boards, meanwhile creating a unique and organized way to share hobbies and interests.
The platform focused on user passions. In this way, it catered to niche communities and fostered organic growth. Today, Pinterest remains a go-to resource for planning projects, recipes, and more.
Here’s a detailed Lean Canvas for Pinterest:
| Problem | Difficulty in discovering, organizing, and saving creative ideas and inspirations online. |
| Solution | A visual discovery platform where users can save, share, and discover creative ideas through “pins” and boards. |
| Unique Selling Proposition | “A virtual pinboard for all your inspirations” — Personalized, visually appealing content and easy organization of ideas. |
| Unfair Advantage | High user engagement through personalized recommendations, strong brand community, and extensive database of user-generated content. |
| Customer Segments | DIY enthusiasts, home decorators, chefs, fashion lovers, wedding planners, and marketers seeking inspiration. |
| Existing Alternatives | Google Images, Instagram, Tumblr, and other social media platforms. |
| Key Metrics | Number of active users, number of pins and boards created, user engagement (likes, repins, comments), and time spent on the platform. |
| High-Level Concept | “A digital mood board” — A social network for discovering and organizing creative ideas visually. |
| Channels | Organic search (SEO), social media, influencer marketing, and partnerships with brands for sponsored content. |
| Early Adopters | Creatives, artists, bloggers, and people interested in lifestyle, fashion, and design. |
| Cost Structure | Platform development, cloud infrastructure, advertising, licensing content, and customer support. |
| Revenue Stream | Advertising revenue from promoted pins, affiliate marketing, and partnerships with brands for content promotion. |
Advantages of Implementing the Lean Canvas Model
The lean canvas model creates the main cornerstone of your business on a one-page template. Improved problem-solving and better planning are only a few benefits this method offers to startups.
So, let’s examine the advantages of the lean canvas model.
Benefit 1: Greater Flexibility
Traditional business models do require much time. Thorough market and competitor research, financial analysis, and other activities take much time and resources. And what is even worse is that you can’t make any changes here. The lean canvas model template doesn’t have a precise framework for your business development. It provides a kind of wireframe that you can adjust to your business. It’s possible to test your idea multiple times and make as many changes as you want.
Benefit 2: Focus on a Problem
By understanding your client’s needs and pain points, you’ll conquer the market in one go. The lean canvas model helps you to develop a unique selling proposition, stand out from the crowd, and outpace your competitors.
Benefit 3: Viable Result Metrics
Analyzing the results of your hard work is one of the keys to building a prosperous company. So, viable result metrics will help you with this task. The lean canvas model equips you with the tools to monitor your buyers’ behavior and the way they interact with your products and services.
Final Note
We provided you with an overview of the lean canvas model and outlined the key benefits of this methodology. Also, we draw you 5 lean canvas examples of multi-billion companies with detailed graphs and figures.
It’s always up to you what goals to set and how to develop your business. By deciding to apply the lean canvas model, you get a time-saving approach to planning and strategizing that will provide you with lots of insights and benefits.
Thus, if you’ve been wondering whether you should use a lean canvas model, our answer is: ‘Yes, you should’. And what could be more important in your business than having a reliable technical partner? By reaching out to LITSLINK, a top software development company