As a member of the Litslink team, attending the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) in San Diego is one of the most critical parts of my year. If you’re involved in the industry, you know NeurIPS is the premier stage for AI research papers and scholarly articles on artificial intelligence. It is the gold standard—the global gathering where leading academics and innovators present peer-reviewed articles on artificial intelligence that define the future of technology. This year, the sheer volume of submissions was staggering. Thousands of scientific articles about AI were reviewed, making the final selection incredibly competitive.
I spent my time diving deep into the latest research papers on artificial intelligence to separate hype from reality. For me, filtering through these artificial intelligence research articles is essential to understanding not just where the technology is today, but where it will be in three years. In this article, I want to share my personal breakdown of the best research papers on artificial intelligence presented at NeurIPS 2025. I will explore the deep technical mechanics of these winners and analyze the research paper topics in AI most relevant for future startups and specific business sectors.
1. Does Reinforcement Learning Really Incentivize Reasoning Capacity in LLMs Beyond the Base Model?
| Category | Details |
| Award | Outstanding Paper Award Runner-Up |
| Authors | Yang Yue · Zhiqi Chen · Rui Lu · Andrew Zhao · Zhaokai Wang · Yang Yue · Shiji Song · Gao Huang |
| Affiliation | LeapLab, Tsinghua University |
| Country | China |
| Resources | Read Paper • Project Page |
This is one of the most discussed research paper topics on artificial intelligence this year. It addresses a practical question: Does Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) make models smarter?
My takeaway from this new research paper on artificial intelligence is sobering. For months, we’ve relied on RLHF to improve model behavior. However, among the scholarly articles about AI presented, this one argues that the reasoning improvement in RLHF-tuned models often doesn’t come from the RL process itself. Instead, the gains are largely attributable to the data used for Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) before the RL step.
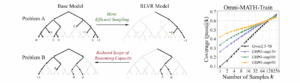
The table below summarizes the critical findings of the paper regarding where “intelligence” actually comes from:
| Feature | Base Model + SFT | Model + RLHF | Improvement Source |
| Logic & Math Ability | High | High (No significant change) | Data Quality (SFT) |
| Formatting & Style | Basic | Professional / Polished | Reinforcement Learning |
| Safety & Alignment | Low | High | Reinforcement Learning |
| Reasoning “Depth” | Base Level | Base Level | Pre-training |
Why This Matters for EdTech and Legal Startups:
For startups in the Educational Technology (EdTech) or Legal Tech sectors, this distinction is vital. If you are building an AI tutor meant to teach calculus, or a legal bot meant to derive case law logic, you cannot rely on RLHF to magically fix a model’s inability to reason. This research suggests that EdTech startups should invest their capital in curating high-quality, step-by-step reasoning datasets for Supervised Fine-Tuning rather than burning cash on expensive RL feedback loops.
2. Gated Attention for Large Language Models: Non-linearity, Sparsity, and Attention-Sink-Free
| Category | Details |
| Recognition | Spotlight Research Selection |
| Authors | Zihan Qiu · Zekun Wang · Bo Zheng · Zeyu Huang · Kaiyue Wen · Songlin Yang · Rui Men · Le Yu · Fei Huang · Suozhi Huang · Dayiheng Liu · Jingren Zhou · Junyang Lin |
| Affiliation | Qwen Team, Alibaba Group |
| Country | China |
| Resources | Read Paper |
The “Attention” mechanism is the engine of the Transformer architecture, but it has a notorious flaw: it is computationally heavy. In standard transformers, the attention mechanism scales quadratically with the sequence length. I was excited to see this paper selected as a Spotlight because it introduces Gated Attention (GA), a technical breakthrough that directly addresses efficiency problems.
The authors propose a mechanism that acts like a cognitive filter. In a standard model, every token (word) pays attention to every previous token. Gated Attention introduces a non-linear “gate” that allows the model to selectively ignore information that is deemed irrelevant for the current context.
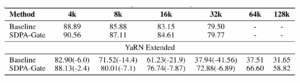
Why This Matters for Mobile App Developers and SaaS:
This is a game-changer for Mobile App Startups focused on “Edge AI”—running AI directly on a user’s phone rather than in the cloud. The reduction in memory usage provided by Gated Attention could allow powerful LLMs to run smoothly on an iPhone or Android device, ensuring user privacy and zero latency.
3. Superposition Yields Robust Neural Scaling
| Category | Details |
| Award | Outstanding Paper Award Runner-Up |
| Authors | Yizhou Liu · Ziming Liu · Jeff Gore |
| Affiliation | MIT / Harvard University |
| Country | USA |
| Resources | Read Paper • Project Page |
This paper was recognized as a Runner-Up for its exceptional contribution to fundamental research among scholarly articles about artificial intelligence. It tackles a concept known as “superposition,” which is essentially the AI version of data compression inside a brain.
The groundbreaking finding here is the link between this superposition and robustness. The authors demonstrate that as you scale a model up (make it larger), it utilizes superposition to become incredibly resistant to noise and damage. If you delete a percentage of the neurons in a large, superposition-heavy model, the performance doesn’t crash; it degrades gracefully.
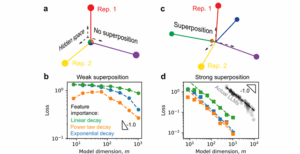
Why This Matters for Healthcare and Autonomous Vehicle Companies:
This research is critical for Healthcare MedTech and Autonomous Vehicle startups. In these fields, system failure is not an option. A self-driving car cannot crash just because one sensor sends “noisy” data. Understanding that superposition yields robustness allows engineers to design architectures that intentionally maximize this property.
4. 1000 Layer Networks for Self-Supervised RL: Scaling Depth Can Enable New Goal-Reaching Capabilities
| Category | Details |
| Award | Outstanding Paper Award Runner-Up |
| Authors | Kevin Wang, Ishaan Javali, Michał Bortkiewicz, Tomasz Trzciński, Benjamin Eysenbach |
| Affiliation | Princeton University / University of Warsaw |
| Country | USA / Poland |
| Resources | Read Paper • Project Page |
Securing a Runner-Up position in the list of the latest research papers in AI, this work challenges the conventional wisdom of neural network architecture. The researchers successfully trained networks with an astounding 1000 layers.
The technical breakthrough here lies in how depth affects “temporal abstraction.” Shallow networks struggle to plan far into the future because the signal gets lost. A 1000-layer network, however, develops a hierarchical understanding of time and tasks.
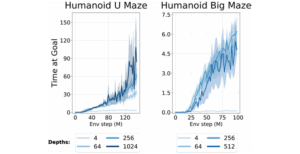
Here is a breakdown of capabilities based on network depth:
| Network Depth | Planning Horizon | Suitable Tasks |
| Shallow (10-50 Layers) | Short-term (Reactive) | Avoiding obstacles, simple grasping |
| Medium (100-300 Layers) | Medium-term | Navigation, simple assembly |
| Ultra-Deep (1000+ Layers) | Long-term (Strategic) | Multi-stage cooking, complex logistics, and tool use |
Why This Matters for Robotics and Logistics Automation:
This is the roadmap for the next generation of Robotics startups and Logistics Automation firms. Currently, most warehouse robots are “reactive”—they see an obstacle and stop. This research opens the door for “planning” robots that can understand complex, long-horizon missions, like cleaning a kitchen, which involves hundreds of small, dependent sub-tasks.
5. Optimal Mistake Bounds for Transductive Online Learning
| Category | Details |
| Award | Outstanding Paper Award (Main Winner) |
| Authors | Zachary Chase, Steve Hanneke, Shay Moran, Jonathan Shafer |
| Affiliation | Technion / Purdue University / UC Berkeley |
| Country | Israel / USA |
| Resources | Read Paper |
This paper took home the top prize—the Outstanding Paper Award. It is a theoretical masterpiece that addresses reliability in learning systems. The paper focuses on Transductive Online Learning, where the AI sees questions but not answers beforehand, and must learn from its errors instantly.
The authors derive a mathematical proof establishing the absolute limit of mistakes an algorithm must make. This moves AI from “empirical alchemy” to a rigorous science. By establishing the “Optimal Mistake Bound,” the paper provides a yardstick for performance.
Why This Matters for FinTech and Cybersecurity:
For FinTech startups dealing with high-frequency trading or Cybersecurity firms fighting zero-day exploits, this is crucial. These industries rely on systems that update in milliseconds. This paper provides the mathematical foundation to build fraud detection systems with guaranteed performance limits. A cybersecurity startup can use these findings to market its threat detection AI as “mathematically optimal” in minimizing false negatives.
6. Artificial Hivemind: The Open-Ended Homogeneity of Language Models (and Beyond)
| Category | Details |
| Award | Outstanding Paper Award Runner-Up |
| Authors | Liwei Jiang · Yuanjun Chai · Margaret Li · Mickel Liu · Raymond Fok · Nouha Dziri · Yulia Tsvetkov · Maarten Sap · Yejin Choi |
| Affiliation | Allen Institute for AI (AI2) / University of Washington |
| Country | USA |
| Resources | Read Paper |
This paper dives into a fascinating sociological and technical topic: homogeneity. It explores how models trained on similar public internet data and fine-tuned with similar human feedback tend to converge into an “Artificial Hivemind.”
The researchers analyzed the outputs of various leading LLMs and found a startling degree of similarity in their opinions, writing styles, and problem-solving approaches.
Why This Matters for Creative Agencies and Specialized Consultants:
This is a warning bell for Creative AI startups. If you are building a tool for scriptwriting or niche scientific innovation, relying on general-purpose foundation models will result in generic outputs. Future startups will succeed not by wrapping a wrapper around GPT-5, but by curating highly specific, proprietary datasets that sit outside the public Hivemind.
7. Why Diffusion Models Don’t Memorize: The Role of Implicit Dynamical Regularization in Training
| Category | Details |
| Award | Outstanding Paper Award Runner-Up |
| Authors | Tony Bonnaire, Raphaël Urfin, Giulio Biroli, Marc Mézard |
| Affiliation | Bocconi University / École Normale Supérieure (Paris) |
| Country | Italy / France |
| Resources | Read Paper |
If you are looking for a generative AI research paper, this Runner-Up winner is the one to read. It tackles the massive legal and ethical fear that image generators simply “memorize” and regurgitate training data.
The key finding is “Implicit Dynamical Regularization.” The training process of a diffusion model involves adding noise and then learning to reverse it. This chaotic process acts as a natural filter, forcing the model to learn generalizable rules rather than specific pixels.
Why This Matters for Enterprise Marketing and Stock Content Platforms:
This research is the legal shield that Enterprise Marketing Platforms have been waiting for. Corporations are terrified of using GenAI due to copyright fears. This paper provides the scientific evidence to argue that diffusion models are legally safe tools. Startups building “Safe GenAI” can cite this research to assure General Counsels that their generative tools are mathematically predisposed against plagiarism.
Key Conclusions from NeurIPS 2025 Winners
My time at NeurIPS 2025 and my review of these latest research papers in AI reinforced several key trends that are shaping the industry:
-
Reasoning requires a new approach
As seen in the research paper on artificial intelligence topics regarding (RLHF), we cannot simply “train” reasoning into a model via feedback; we need better data foundations. -
Efficiency is the new performance
Architectural changes like Gated Attention are essential for the economic viability of AI companies. -
Reliability through Math
Theoretical work, like the Main Winner on Mistake Bounds, provides the rules that make artificial intelligence research paper topics a reality, moving us from experimental to engineering phases.
Litslink: Translating Advanced Research into Business Value
The insights I’ve gathered from these groundbreaking AI research papers at NeurIPS 2025 are what define our approach at Litslink. We don’t just read the abstracts; we dive into the code and the proofs found in scholarly articles about AI to understand how to apply them directly to our clients’ toughest business challenges.
The AI landscape is moving too fast for businesses to rely on generic solutions. We specialize in taking the insights from the best research papers on artificial intelligence—like optimizing models based on new insights into Superposition or building deep RL agents—and turning them into scalable, high-impact Artificial Intelligence Services.
If you’re looking to integrate AI that goes beyond basic chatbots, Litslink offers the deep technical expertise needed to utilize these NeurIPS-level breakthroughs. We help you design, build, and deploy custom AI solutions that incorporate the latest efficiency, reasoning, and safety mechanisms to deliver measurable ROI and a genuine competitive edge in your industry.





