Computer vision (CV) is an example of a revolutionary technology generating significant interest, specifically in medical imaging.
This blog post explores the impact of computer vision in healthcare, its applications, and the development process of an AI diagnostic instrument designed for medical image analysis.
Understanding Computer Vision in Healthcare
Computer vision, which falls under the umbrella of AI, enables machines to process visual data for interpretation and decision-making purposes. This ultimately allows healthcare professionals to make precise and timely diagnoses and develop effective treatment plans by enabling the analysis of medical images with remarkable speed and accuracy. AI medical diagnosis tools enhance this process further by offering deeper insights and identifying patterns that might be missed by the human eye, ensuring more accurate and personalized care for patients.
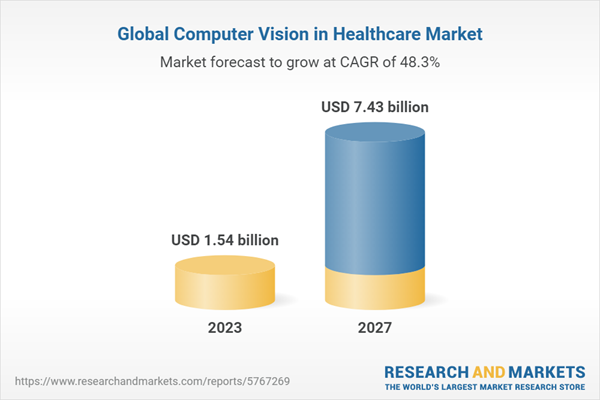
Currently, the global market for computer vision in healthcare is on a robust expansion trajectory, showing promising growth in the next few years.
Computer Vision Applications in Healthcare
Computer vision in healthcare is versatile, transforming how the healthcare sector operates in numerous ways.
- Medical imaging interpretation. Diligent medical images, including X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, are areas where computer vision truly stands out, providing valuable insights for enhanced diagnostic accuracy.
- Custom healthcare software solutions. In the healthcare AI market, software holds a larger share than hardware and services.
Custom software solutions that utilize AI computer vision are currently being created to address distinct healthcare requirements. Prominent organizations such as IBM Watson Health are at the forefront of developing bespoke healthcare software solutions, thereby demonstrating computer vision’s versatility in tackling a wide range of medical challenges.
- Early disease detection. With the ability to identify diseases early on, AI-powered diagnostic tools can detect minute irregularities in medical images. According to a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), AI algorithms outperformed radiologists in diagnosing breast cancer from mammograms.
- Drug discovery and development. Computer vision in medicine expedites drug discovery by analyzing vast datasets of molecular and cellular interactions. It assists researchers in identifying potential drug candidates and predicting their efficacy, significantly reducing the time and resources required for drug development.
- Personalized medicine. Computer vision contributes to personalized medicine by analyzing patient-specific data, including genetic information and medical images. This allows healthcare professionals to tailor treatment plans based on individual characteristics, optimizing therapeutic outcomes. AI in Pharma further enhances this process by accelerating drug discovery, improving clinical trial designs, and enabling more precise medication development, ultimately leading to more effective treatments for patients.
- Surgical assistance. Surgeons benefit from medical computer vision by gaining insights in real-time throughout procedures, which increases accuracy and decreases potential risks. Grand View Research projects that the surgical display market will surpass $700 million by 2028.
- Fall detection and elderly care. In elderly care, medical computer vision aids in fall detection through video analysis. Recognizing irregular movement patterns enhances the safety of elderly individuals, offering timely assistance in case of a fall.
- Administrative efficiency. Computer vision is streamlining administrative tasks in healthcare facilities, from automating patient check-ins to inventory management. This not only improves operational efficiency but also reduces the burden on administrative staff.
- Behavioral health monitoring. Medical computer vision analyzes facial expressions, gestures, and speech patterns to provide insights into patients’ mental health. This assists healthcare professionals in monitoring behavioral health and tailoring interventions accordingly.
Benefits Of AI Computer Vision In Medical Imaging

The integration of AI and computer vision in medical imaging has ushered in a new era of transformative benefits, revolutionizing the way healthcare professionals approach diagnostics and patient care. Here are the key advantages of leveraging AI computer vision in medical imaging.
Precision in diagnoses
- Benefit: AI-driven computer vision enhances diagnostic precision by meticulously analyzing intricate details within medical images, resulting in consistently accurate and reliable diagnoses.
- Impact: This heightened accuracy proves crucial in complex medical scenarios, enabling healthcare professionals to make well-informed decisions, thereby improving patient outcomes.
Timely detection of diseases
- Benefit: AI algorithms, fueled by medical computer vision capabilities, excel in identifying subtle indicators of diseases during their nascent stages.
- Impact: Early disease detection translates into more effective treatment interventions, potentially altering the course of the disease and improving long-term prognosis for patients.
Streamlined workflow efficiency
- Benefit: Computer vision streamlines the interpretation of intricate medical images, reducing the time and effort needed for analysis.
- Impact: This efficiency gain is not merely a time-saving measure but a strategic improvement, allowing healthcare professionals to dedicate more time to nuanced decision-making and personalized patient care.
Tailored treatment approaches
- Benefit: Precise analysis of medical images enables the customization of treatment plans, aligning interventions with individual patient characteristics.
- Impact: Tailored treatment approaches go beyond a one-size-fits-all model, contributing to optimized therapies and potentially minimizing side effects for patients.
Automation of routine tasks
- Benefit: Computer vision medical imaging automates routine tasks such as image segmentation, allowing healthcare professionals to focus on complex decision-making.
- Impact: Beyond time efficiency, this automation elevates the role of healthcare practitioners, empowering them to leverage their expertise where it matters most in patient care.
Access to specialized expertise
- Benefit: Computer vision in medicine extends specialized expertise to areas with limited access to healthcare resources, overcoming geographical barriers.
- Impact: This democratization of expertise ensures that patients in underserved regions receive timely and accurate diagnostics, contributing to improved healthcare equity.
Continuous learning and improvement
- Benefit: Machine learning algorithms, integral to AI, continuously learn and adapt, refining diagnostic capabilities over time.
- Impact: This continuous learning ensures that the AI system evolves alongside medical advancements, adapting to emerging challenges and maintaining relevance in dynamic healthcare landscapes.
Mitigation of diagnostic errors
- Benefit: Systematic application of computer vision in the medical field significantly reduces diagnostic errors, promoting a safer healthcare environment.
- Impact: Minimizing errors not only improves patient safety but also reduces the financial and emotional burden associated with corrective measures for misdiagnoses.
Cost-efficiency and resource optimization
- Benefit: Computer vision in the medical field optimizes resource utilization, contributing to overall cost-efficiency in healthcare facilities.
- Impact: This resource optimization ensures that limited resources are allocated strategically, maximizing the impact on patient care and overall operational efficiency.
Integration with emerging technologies
- Benefit: Computer vision seamlessly integrates with emerging technologies like 5G and edge computing.
- Impact: This integration propels medical image analysis into real-time processing capabilities, fostering new possibilities for swift and efficient diagnostics in rapidly evolving healthcare ecosystems.
As healthcare continues to evolve, these benefits position AI computer vision medical imaging as a key contributor, shaping a future where diagnostics are not only precise but also profoundly informed and patient-centric. AI in Healthcare further amplifies this transformation by streamlining workflows, enhancing early detection capabilities, and providing real-time, data-driven insights, thereby improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
Creating an AI Diagnostic Tool: Step by Step

Crafting an AI diagnostic tool involves leveraging artificial intelligence services and medical image analysis. Here are four essential steps to create an AI diagnostic tool:
Step 1: Data Collection and Preparation
Building a solid AI diagnostic tool requires a large and varied dataset of medical images. This dataset serves as the foundation for training the machine learning model.
Key considerations:
- Ensure the dataset includes a variety of medical conditions and demographics to enhance the model’s generalization.
- Precise annotation of images is crucial for supervised learning, where the model learns from labeled examples.
Step 2: Model Selection and Training
The success of AI for medical diagnosis tools is highly dependent on selecting the optimal model architecture. Image-related tasks frequently utilize Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) on account of their capacity to capture complex patterns.
Key considerations:
- Leverage pre-trained models to expedite training and enhance performance.
- Adjust the pre-trained model to the specifics of the medical imaging domain for optimal results.
Step 3: Validation and Testing
Conducting thorough validation and testing is critical to ascertain the model’s dependability and effectiveness in practical situations.
Key considerations:
- Assess the model’s performance across multiple subsets of the dataset to avoid overfitting.
- Evaluate the model using external datasets to simulate real-world conditions.
Step 4: Integration into the Healthcare Workflow
After the AI diagnostic tool has established a strong performance baseline, it becomes critical to integrate it seamlessly into the healthcare workflow.
Key considerations:
- Ensure compatibility with existing healthcare systems for smooth adoption.
- Develop an intuitive interface that facilitates easy interaction for healthcare professionals.
Key Challenges in Creating an AI Diagnostic Tool for Medical Image Analysis
Creating an AI health diagnosis tool is promising but not without its share of challenges. Let’s examine the primary issues when building an application leveraging AI for medical diagnosis.
Limited and diverse data:
- Challenge: All AI model training efforts must have access to large, varied datasets. Insufficient or biased datasets can cause models not to be applicable to a wider range of situations.
- Solution: Gain access to and collect huge datasets that are diverse in nature and cover a wide range of medical conditions, demographics, and imaging modalities.
Data privacy and security:
- Challenge: The security and privacy of patient information is a major concern due to the sensitive nature of medical pictures. The healthcare industry has stringent laws that must be followed.
- Solution: Implement robust encryption, anonymization, and access control measures to safeguard patient data. Adhere to healthcare data protection regulations.
Interpretability and explainability:
- Challenge: AI models, especially deep learning models, are often perceived as “black boxes,” making it challenging for healthcare professionals to understand and trust their decisions.
- Solution: Focus on developing models with interpretable features. Utilize techniques such as attention mechanisms to highlight regions of interest in medical images.
Integration with existing healthcare systems:
- Challenge: Incorporating AI diagnostic tools into preexisting healthcare procedures and systems can be complicated without causing disruptions, especially when dealing with incompatible technologies.
- Solution: Collaborate with healthcare IT professionals to ensure interoperability. Develop user-friendly interfaces that align with existing workflows.
Regulatory compliance:
- Challenge: Meeting regulatory standards and obtaining necessary approvals for medical AI tools requires compliance with regional healthcare regulations.
- Solution: Engage with regulatory bodies early in the development process, ensuring adherence to guidelines and standards for medical device approval.
Limited clinical validation:
- Challenge: The lack of extensive clinical trials and real-world validation prevents healthcare practitioners from fully embracing and using artificial intelligence in medical diagnosis.
- Solution: Conduct rigorous clinical trials to validate the accuracy and efficacy of the AI tool. Collaborate with healthcare institutions for real-world testing.
Resource dependence:
- Challenge: Developing, training, and maintaining AI models for medical image analysis can be resource-intensive, requiring substantial computational power and expertise.
- Solution: Leverage cloud computing resources, collaborate with institutions with computational capabilities, and explore partnerships with AI research organizations.
User acceptance and training:
- Challenge: Healthcare professionals may resist adopting AI tools due to a lack of understanding or trust in the technology.
- Solution: Provide comprehensive training programs to familiarize healthcare professionals with the AI tool’s capabilities and limitations. Foster a culture of collaboration between AI and medical experts.
Addressing all the listed challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach involving collaboration between computer scientists, healthcare professionals, and regulatory bodies. As technology advances, overcoming these challenges is crucial for realizing the full potential of AI diagnostic tools in enhancing medical image analysis and improving patient care.
Final Thoughts
Medical diagnosis may undergo a radical shift due to the advent of computer vision, which is more than just a fad in the healthcare industry. Healthcare computer vision has numerous different and significant applications, ranging from early disease detection to individualized treatment plans. The benefits of using AI in this context are immense, as it enables faster, more accurate diagnoses, reduces human error, and facilitates personalized care that can lead to better patient outcomes.
Working together, AI and healthcare providers hold the key to a future where faster, more precise diagnoses lead to better health outcomes for patients. A better, more technologically empowered future is within reach if we seize the opportunity to develop AI health diagnosis tools for medical picture analysis.