Optimization lies at the core of successful manufacturing. Whether it’s maximizing productivity, ensuring strict quality control, minimizing costs, or managing compliance risks, manufacturers must continually refine their processes to stay competitive. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is increasingly the solution of choice, revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape through powerful tools such as machine learning, predictive analytics, computer vision, and automation.
AI is not merely an innovation; it’s reshaping manufacturing from the ground up. It enhances efficiency, precision, and flexibility across various operations, aligning perfectly with Industry 4.0 objectives. Manufacturers leveraging AI experience reduced downtime, improved product quality, optimized supply chains, and significant cost savings.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into real-world use cases, tangible benefits, statistical insights, and practical strategies for integrating AI into your manufacturing processes. By exploring successful examples and addressing common challenges, we’ll help you understand whether AI in manufacturing is a lasting solution or merely temporary hype. Join us as we examine how AI can transform your business operations today and position you for sustainable growth tomorrow.
Insights into AI in Manufacturing
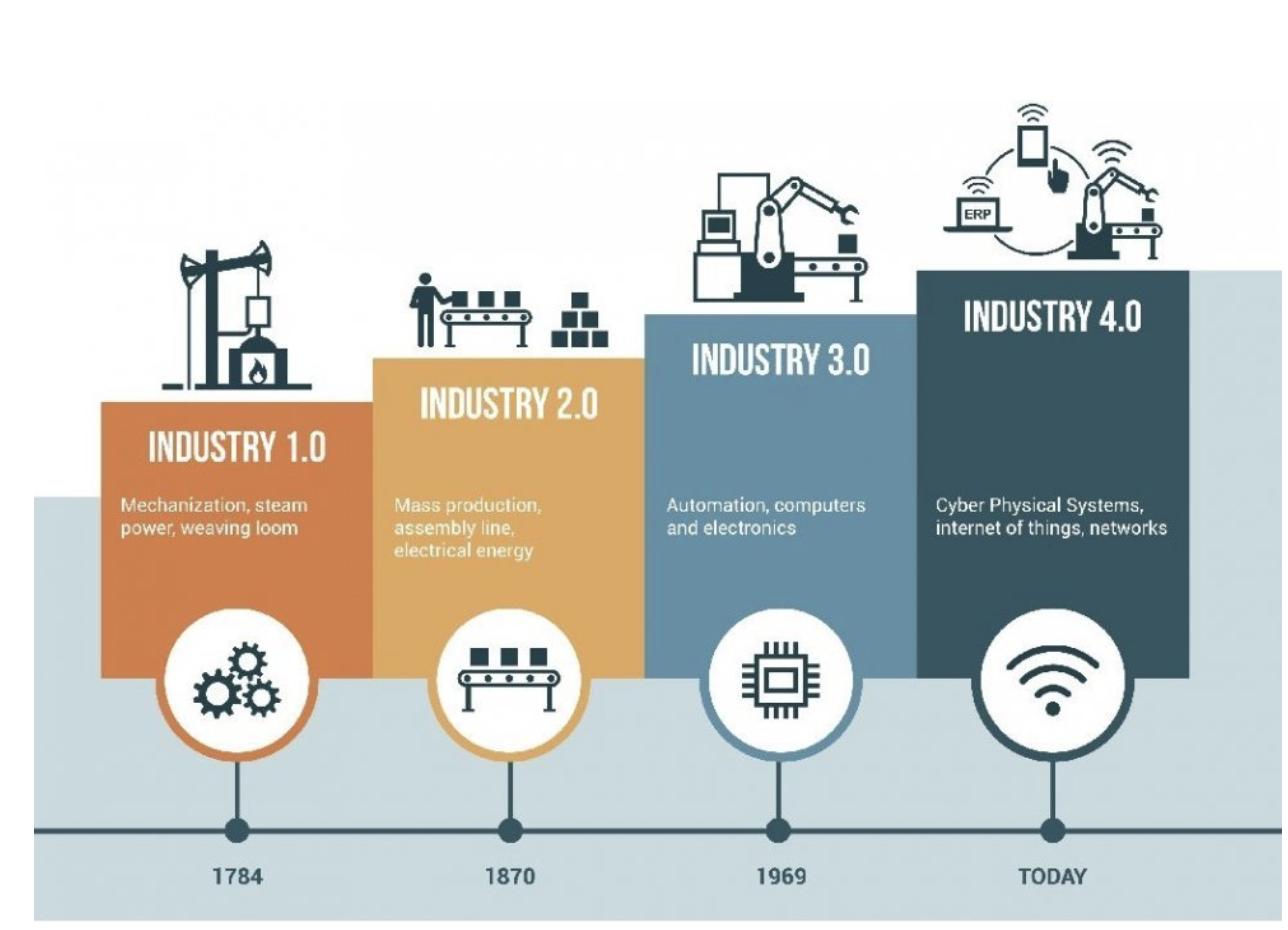
The theory of artificial intelligence for manufacturing, by and large, embodies robot-filled work environments where human workers and machines operate shoulder to shoulder. This concept has been established in human minds since the 1960s. But in 2025, it is a reality. It’s all about data and analytics that authorize better predictions and/or decision-making at all stages of manufacturing processes. Not to be empty-worded, here’s some statistics:
- In 2023, the universal Artificial Intelligence in the manufacturing market reached 3.2 billion USD.
- By 2028, the worldwide AI in the manufacturing market is predicted to grow to 20.8 billion USD.
- 30% of large manufacturing companies earning over 10 billion USD yearly and 10% of companies earning under 10 billion USD (between 500 million and 10 billion USD yearly) have established generative AI use cases and witnessed positive business results.
- According to Forbes Advisory, 56% of surveyed businesses use AI tools to enhance their operations.
- According to Deloitte’s survey, 93% of companies are convinced that AI is a pivotal technology that can foster innovation and growth in the manufacturing process.
- 27% of companies believe that AI systems have brought value to operations, while 56% expect to see first results in 2 to 5 years.
- 66% of manufacturers who have introduced AI instruments to their daily operations reported high dependency on transformative technologies and suggested continuing to adopt AI in their sector.
The concern in AI applications in manufacturing is whether AI-based systems will make business owners rely more on the new technology and turn away the human workforce. The real picture is quite the opposite:
- In the near future, the new technology is predicted to create more than 12,000,000 more job opportunities than AI is expected to replace.
- By 2025, 97,00,000 experts will be in demand for the AI industry.
- According to eMarket, 69% of people in leadership roles believe that Artificial Intelligence will result in the appearance of new job opportunities.
This data looks encouraging, notwithstanding some pessimistic impressions of AI that you and other businesses may have.
How Is AI Used in Manufacturing?
You’ll be surprised at the number of AI use cases in manufacturing. Before we dive into each use case, let’s focus on the market scope of such cases across geographies.
| Coverage | Details |
| 2023 market size | USD 5.07 billion |
| 2032 market size | USD 68.36 billion |
| Forecast period | 2023-2032 |
| 2023-2032 growth rate | CAGR of 33.5% |
| Largest use case market | North America |
| Fastest growing use case market | Asia-Pacific |
| Base Year | 2022 |
| Segments covered | by technology/offering/application/industry |
| Regions covered | North America, Asia-Pacific, Europe, Middle East, Africa, Latin America |

Supply Chain Management
30% of businesses are turning to Artificial Intelligence tools for their bookkeeping and management of retail chain operations.
Supply chain disruptions are prevalent across manufacturing plants. The use of AI in the manufacturing industry has resulted in a real shake-up. By applying the power of AI instruments and programs, a factory can alter its processes and improve accuracy, cost-efficiency, and effectiveness.
AI in manufacturing use cases helps to leverage performance analytics, enhance demand forecasting, streamline logistics, and optimize inventory management. Because of Machine Learning algorithms, companies can scrutinize all figures, ferret out patterns, and foretell demand fluctuations.
Cobots
AI’s share in industrial robotics is expected to reach 10.72 billion USD in 2024 and a market volume of 20.64 billion USD by 2030.
The notion of cobots (collaborative robots) is relatively new to the manufacturing sector. This AI-driven technology is applied across fulfillment centers to help with picking and packing. What’s more, cobots run in parallel with employees and spot objects through an inbuilt AI system.
Cobots are an example of the huge impact of AI in the manufacturing industry. They perform complex tasks, are accurate and responsive, handle challenging assembly line flows, and carry out quality control surveys. These robotic workers have become invaluable when it comes to minimizing downtime or reducing maintenance costs.

Predictive Maintenance
If the breakdown is correctly forecasted, employees can timely redistribute production loads on different machines while fixing a machine in question. This precautionary maintenance retains around 40% of repair costs.
Smart factories leverage advanced predictive analytics and ML algorithms as the element of their use of Artificial Intelligence in manufacturing. This licenses a manufacturer to dynamically screen and forecast machine failures, thus minimizing possible downtimes and working across an optimized maintenance agenda.
Using AI in manufacturing, staff can enforce a digital twin, a virtual replica of a real engine, harvesting and processing data and imitating asset behavior in a virtual equipment setting. In particular, the Ford factory is well-known for introducing digital twins as part of its digital transformation campaign. Twins help with energy loss identification, defect detention, and overall production line performance.
Performance Optimization
Operators who applied artificial Intelligence in the manufacturing industry reported a 10% to 15% boost in the production process and a 4% to 5% increase in EBITA.
Implementing AI in optimizing performance is another game changer. AI algorithms help to make only data-supported decisions, thus optimizing operations, reducing downtime, and maximizing the overall effectiveness of machinery.
An appropriate example of AI in manufacturing is General Electric and its AI algorithms, which were introduced to analyze massive data sets, both historical records and up-to-date data sets. With the assistance of AI in the manufacturing process, General Electric has instant access to trends, predicts equipment issues, boosts equipment effectiveness, and improves operations efficiency.
Quality Assurance
60% of interviewed industrialists are applying AI tools for quality monitoring and are said to detect 200% more supply chain disruption than before AI use in manufacturing.
AI in the manufacturing sector has revolutionized businesses’ approach to quality control. After the application of AI, the levels of alignment and accuracy have grown many times. The thing is that with AI, manufacturers make use of computer vision algorithms that analyze videos and pictures of products and their parts.
Executed algorithms run with distinguished precision, pinpointing anomalies, shortcomings, or deviations from accepted quality standards. Here, human competencies are far surpassed. Additionally, by analyzing historical data, algorithms facilitate addressing flaws, allowing manufacturers to take restorative actions before any impact.

Streamlined Paperwork
Paperless production raises real-time presence and product quality by shifting paper documents to digital records. 4 out of 6 manufacturers have already switched to digital records.
Another industry trend is the application of advanced ML algorithms in manufacturing and the use of RPA for administrative work automation. Manufacturing used to involve invoices, purchase orders, quality control reports, and lots of other paperwork. With the application of AI in manufacturing, most manual, error-prone, and time-consuming processes were substituted to enhance factory efficiency.
Companies use intelligent bots with AI capabilities to automatically collect data and extract it from papers, classify information, categorize it, and then enter it into relevant systems. RPA bots carry out most repetitive tasks or rule-based duties with correctness and efficiency.
Benefits of AI in Manufacturing
Here’s a brief overview of 8 key benefits of AI and Machine Learning in manufacturing:
- Increased productivity among employees, as they now need less time on repetitive tasks or mundane work.
- A more innovative and efficient design process since the system creates different variations for operators.
- Reinforced consumer expectations due to improved CX at different points along the customer journey.
- Improved inventory management and demand forecasting, as well as reduces errors in supply chain networks by 50%.
- Augmented quality monitoring, in contrast to the cases missed by humans.
- Predictive maintenance thanks to large volumes of captured and analyzed data.
- Round-the-clock manufacturing with a high degree of accuracy.
- Modernized factory layouts and well-designed factory floors for maximum production process efficiency.
AI in Manufacturing Examples: Big Cases
Let’s check how big market players use AI in manufacturing.
Toyota
For its North American factories, Toyota decided to collaborate with Invisible AI and introduce computer vision to its manufacturing sector. This made the production process more efficient, higher in quality, and safer for the multiple employees working there.
The introduced AI solutions can learn by themselves without any connection to the Internet or cloud. These AI tools are developed with the newest technology and have high-resolution cameras to watch over everything on the floor.
General Electric (GE)
General Electric has started using AI in manufacturing to reduce design times. With AI technology, their engineers can create tools to streamline the process of designing power turbines and jet engines.
In fact, GE employees required only 48 hours to analyze the movement of fluids in a turbine blade and engine part design. Then, they developed a model to assess millions of design deviations in 15 minutes. Ultimately, this allowed them to intensify the creation of the company’s next product line.
Suntory PepsiCo
Suntory PepsiCo witnessed another impact of AI in manufacturing. With five factories in Vietnam, they needed assistance reading soda drink labels with smudged manufacturing and expiration dates.
To prevent delays and additional production expenses, they started using the Machine Vision solution, which uses cameras to quickly read, check, and correct smudged or missing labels. If humans had to do the same, it would take more time, while with AI, mistakes and expenses are fewer.
The Future of AI in Manufacturing
The future of Artificial Intelligence in manufacturing industries looks very promising. To begin with, there are three main directions where AI in manufacturing is going to bring the highest value:
-
- AI is expected to revamp how plants and factories work. Advanced technologies will soon improve the efficiency of traditional manufacturing, consolidating data in one place, integrating data from equipment, and bringing it into environments where it’ll be combined with other data.
- Decision-making will be AI-driven. Data collaboration is expected to be introduced in the next few years, where gathering and combining information across teams and empowering experts to provide unique insights will be the norm.
- Forward-looking data strategies will become must-haves. It will also become a norm to combine, store, govern, and manage data in one platform to streamline adjustments to a quickly evolving competitive environment.
Here are some statistical insights and predictions for the future role of Artificial Intelligence in manufacturing:
- By 2030, generative AI is expected to automate 30% of working hours.
- Thanks to AI, China can expect a 26% GDP boost by 2030.
- By 2025, errors in forecasting may decrease by 20%.
- In the next 10 years, AI is expected to save 1.3 trillion USD and 2.6 trillion USD in cost reduction while reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 2.6 to 5.3 gigatons of CO2.
- By 2035, AI technologies will help to raise production by 40%.
Bottom Line
As you can see, the uses of artificial intelligence in manufacturing are diverse. In fact, there’s hardly a sector where implementing AI would be a bad idea. Those eager to address current manufacturing issues and move alongside their competitors are now weighing the pros and cons of adopting AI for their manufacturing operations. At LITSLINK, we practice a respective and adaptive approach following the Scrum Framework to develop AI-powered projects that reflect the needs of your production. Contact our manager and open the door to AI today.