Did you know that by 2025, 95% of all enterprise workloads will be in the cloud? This staggering statistic underscores the monumental shift towards cloud computing as the backbone of modern business operations.
As organizations increasingly embrace the cloud to drive innovation, scalability, and efficiency, it’s imperative to understand the fundamental difference between IaaS, and PaaS SaaS.
These three pillars of cloud computing offer distinct advantages and cater to diverse business needs. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll unravel the complexities of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your cloud strategy.
Whether you’re a seasoned IT professional or a curious newcomer to the world of cloud computing, join us as we navigate through the intricacies of cloud service models and explore their implications for modern businesses.
What Is IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS?
Let’s start to explain these concepts and describe their key differences from one another. But first, you should understand that all of them fall under the category of “cloud as a service” and how LITSLINK, a top software development company, applies its main principles to cloud app development.
So “cloud as a service” is a virtual environment that interacts with clients (both users and systems) and connects them to various computing services such as storage, networking, and services.
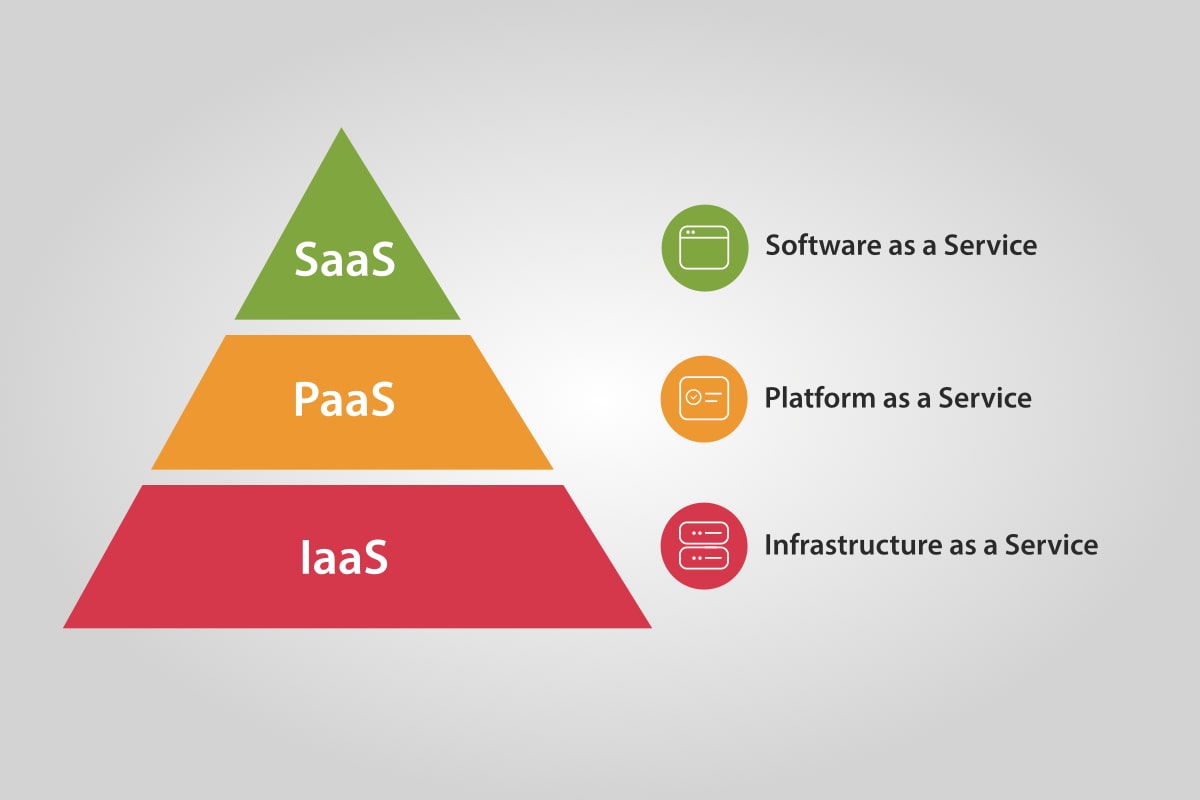
What does IaaS mean? It is an abbreviation for “infrastructure as a service.” This model presupposes the provision of machines, storage space, and network capacity that software engineers and businesses can lease to install the software on which their corporate apps and supportive structures function. In other words, IaaS is a remote data center where a variety of users may rent space for their systems’ setup. After that, they manage and upgrade that system (both hardware and software) on their own.
PaaS is a “platform as a service.” As its name suggests, this model represents a virtual platform on which programmers work on their apps. A typical PaaS usually incorporates hardware (including critical equipment such as servers), a variety of OSs, and a coder’s toolkit for software creation and administration. PaaS resources are managed by the owner, so developers are freed from the hassle of hardware or operating system upgrades – in fact, they rent cloud capacity to perform their tasks.
SaaS stands for “software as a service.” It is a ready-made virtual environment equipped with an intuitive and convenient user interface (UI). In other words, SaaS represents a cloud-based foundation for the creation of any software without excessive coding, only by customizing the front-end features and design. Correspondingly, any software solutions developed with SaaS comprise the web-delivered content accessible by any user via a browser.
So, to recap the distinctions: IaaS is an infrastructure – software and hardware – that powers servers, storage, networks, and operating systems and allows the developers to create their platforms and software. PaaS is a set of tools and services that allow the coding and deployment of applications quickly and efficiently; it possesses a built-in infrastructure and platform, thus allowing the developer to create his/her program and launch it. SaaS is the most advanced form of a cloud service model because it already incorporates the infrastructure, the platform, and the software on demand. Thus, SaaS applications are multi-purpose software already designed with an end user in mind and are delivered over the Web. Because of such flexibility and ready-made functionality, SaaS tools may be easily applied in a variety of niches including e-commerce, education, corporate solutions, etc. At LITSLINK, we are proficient in SaaS and have solid expertise that could be backed by our extensive portfolio of cases. If you want to know more about our top-notch SaaS services, get acquainted with successful IT outsourcing case studies in our blog.
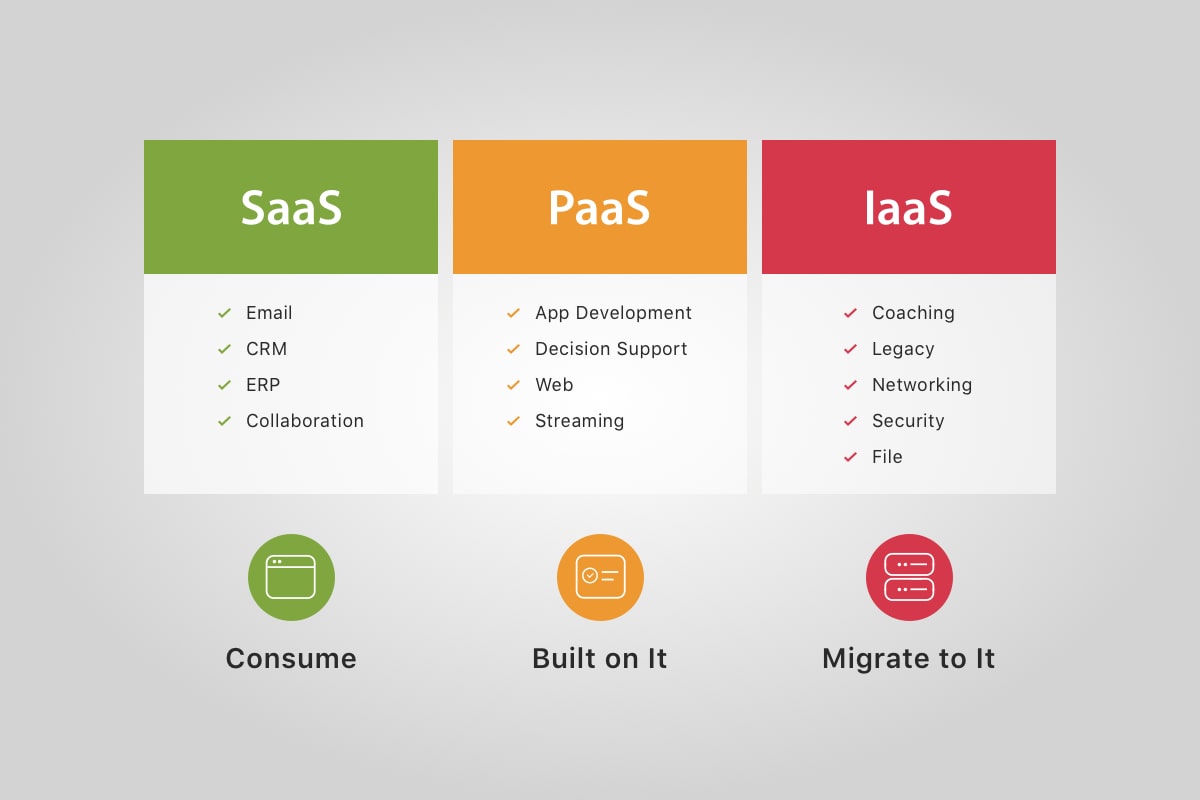
Examples of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
There are few purely PaaS, SaaS, or IaaS examples as many businesses resort to a certain combination thereof depending on their technology needs. Here we give some common cloud services examples popular among developers across the globe and possessing a strong growth potential.
Examples of IaaS: Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2), Cisco Metapod, Microsoft Azure, Google Compute, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Rackspace, Digital Ocean, Magento 1 Enterprise Edition, Joyent. The typical IaaS use-case is the extension of current infrastructure for handling temporary traffic increases (for instance, your e-store faces an enormous increase of site traffic during the Christmas holidays, and you use the IaaS capacity to support its functioning and not to lose profits because of the website’s failure).
SaaS examples: Salesforce, Google Apps, TurboTax, QuickBooks, Workday, Concur, Citrix GoToMeeting, and Cisco WebEx. Google Docs is also an example of software as a service – this application has gained global popularity not only among businesses but among millions of regular Web users. The common case use of SaaS is that of replacing traditional software with on-device, on-demand software accessible through the Web.
PaaS examples: Windows Azure, Google App Engine, Apprenda, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Heroku, Apache Stratos. The typical application of PaaS includes the increase of developer’s productivity and utilization rates combined with the achievement of lower time-to-market of the developed application.
Advantages of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
Now that you know what PaaS, IaaS, and SaaS are and what examples of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS there are in the market, it’s high time to find out what’s good and bad about each of the service models. This information may shed light on their comparative characteristics and help you choose the one that suits your business and software development/use needs the most.
Pros and Cons of IaaS
Using IaaS offers many advantages to the users.
- Cost-effectiveness. IaaS helps to maintain on-premise IT infrastructure that is otherwise too costly and resource-consuming. In traditional systems, purchasing hardware and maintaining your personal infrastructure may involve many expenditures. The hardware is expensive; it has to be operated by an IT specialist, and it also requires regular upgrades to function at its highest capacity. With IaaS, you avoid this trouble and save costs on buying hardware and hiring administrators; the IaaS solution already has it all on a very affordable pay-as-you-go basis.
- Flexibility and scalability. The users of IaaS can easily change the IaaS provider or purchase additional capacity without serious investments or losses, which is impossible in case they own hardware and need to replace it with newer versions.
- User’s control. Using the IaaS solutions does not reduce your control over the infrastructure, leaving it all in your hands. Oversight of IaaS is possible even by an individual developer, which means that you don’t need to hire any additional IT staff to have your infrastructure running smoothly. In case you run into any problems, most IaaS providers offer 24/7 support available for any inquiries.
Some disadvantages of IaaS also need to be mentioned. The basic precondition for the smooth operation of your infrastructure is an Internet connection. Thus, problems with connectivity, weak or unstable Web connection, and other problems will inevitably cause disruptions in the operation of your IaaS environment. Another con is the dependence on virtualization services, which are not always suitable for a user. Finally, IaaS restricts user privacy and customization. Perfect for:
- Startups: Scaling resources on-demand without upfront hardware investment.
- Large enterprises: Running mission-critical applications with maximum flexibility and security.
- Data analytics: Processing massive datasets with scalable computing power.
Pros and Cons of PaaS
Now let’s consider PaaS and its relative strengths and weaknesses. The benefits of using PaaS solutions include:
- Advanced customization. In case you work with PaaS tools, you can easily customize the existing software and app tools for the generation of unique software products. The best part of it is that you don’t need to go through the entire process of software development and code everything; you can use pre-existing templates and frameworks to build your solutions upon them and tailor them to your individual tastes and intentions.
- Cost-effectiveness. While creating a new app is pricey, no business wishes to use some cheap, standard solutions. PaaS provides a unique combination that allows the generation of great apps without spending much money on them due to its extensive tools and scripts serving as a solid basis for quick and cost-effective customization. Get to know the potential price of your app with an app development calculator to ensure you get a cost-effective solution.
- Virtualization and operational efficiency. No matter how much PaaS capacity you need, you are free to utilize it without in-depth system administration skills. The model is intuitive and user-friendly, thus enabling you to scale your software needs depending on business growth without limitations.
Using PaaS nevertheless comes with certain cons such as the risk of lock-in (creating software within a specific PaaS environment ties you to that platform with its interface, programming language, and interface) and limited scalability (PaaS tools are somewhat inflexible in terms of supplies on demand). Besides, experts recommend performing an additional data backup to the one provided by a PaaS environment to prevent data losses in case of any emergency. Ideal for:
- Web and mobile app development: Rapidly building and deploying applications without infrastructure concerns.
- Enterprise software development: Focusing on application logic instead of infrastructure management.
- Content management systems: Easily setting up and scaling content platforms.
Pros and Cons of SaaS
SaaS is currently regarded as the most flexible and accessible of all cloud service models. It is the most popular service among businesses favoring cloud solutions. SaaS benefits include enabling app use by end users without downloading them directly through an Internet browser. In such a way, these apps save precious space on user devices.
SaaS has benefits for both entrepreneurs and coders, such as:
- Simple integration (all you need to start working is a browser; SaaS solutions are equally accessible via desktop and mobile devices);
- Low cost (with the data center residing in the cloud, you don’t need to spend much on the SaaS solutions as compared to paying for the hardware and storage facilities for offline, physical data storage)
- Scalability (users can easily get more cloud space by purchasing additional licenses).
Nevertheless, when talking about SaaS, one should still note that it also has some cons, and the main one is security. Many users still find it risky to store sensitive, confidential corporate information in the cloud because of the hazard of cyber theft and data leakage. Great for:
- CRM and project management: Accessing collaboration tools anytime, anywhere.
- Email and office productivity: Using familiar software without local installations.
Marketing automation: Streamlining marketing campaigns with cloud-based tools.
IaaS vs. PaaS vs. SaaS
It’s also instrumental to find out what distinguishes each cloud service model from the other two counterparts to get a firm grasp of situations in which a certain business needs to choose one of them in favor of the other two.
Difference Between IaaS and PaaS
The basis of the PaaS vs IaaS comparison is that PaaS applications are cloud-ready, and IaaS solutions are cloud-native. Being cloud-ready means that the application can run anywhere on any platform, is highly scalable, and loosely coupled. Moreover, it has to be automated for deployment. Being cloud-native means that an app was initially designed for the application in the cloud environment. In such a way, the IaaS-created app is made to take full advantage of all cloud functionality, which makes it the most suitable solution for the microservice architecture.
Difference Between PaaS and SaaS
When comparing SaaS and PaaS, one should note that the benefit of the former is in the ready-made solution requiring no additional input from the developer. The SaaS provider takes care of everything, while your task is to use the service without taking care of anything behind the scenes, that is, the back end.
The benefit of PaaS (though some users still regard it to be a drawback) is the loose definition of the environment allowing the developer considerable flexibility and freedom of creating his/her own systems. Some experts see the enormous potential of PaaS in terms of creating Web-intensive functions with high cost and low predictability, e.g., e-commerce. However, to realize that potential, PaaS needs to develop and acquire features that a modern e-commerce customer requires, such as user-friendliness, customization, and scalability.
Difference Between IaaS and SaaS
As it was explained above, SaaS is a ready-made software application run directly through the Web browser and does not require any developer input. It is a plug-and-play product that you may use instantly, which is definitely suitable for many business situations.
The only advantage of IaaS as compared to SaaS is the degree of user access to the operational settings and management of the application. While in the SaaS environment, the user has no access to any of the settings, infrastructure, and operational configurations, in IaaS, the user does not participate in the administration of hardware but can adjust the operational and app settings on his/her own. In such a way, users who wish to get more customizable solutions should opt for IaaS instead of SaaS despite its convenience.
Why You Should Use SaaS
The future is SaaS-tactic, and for good reason. Unlike its on-premise counterparts, SaaS offers a plethora of benefits that make it an excellent choice for businesses of all sizes and types. Here’s why you should consider the SaaS route:
- Flexibility and Scalability: Forget rigid software with hefty upgrades. SaaS adapts to your needs, scaling up or down seamlessly as your business grows. Need more users? Done! Facing a seasonal dip? Adjust your subscription accordingly.
- Affordability and Lower Risk: No upfront infrastructure costs, no expensive installations, and predictable subscription fees make SaaS a budget-friendly choice. Ditch the upfront investment and pay only for what you use, minimizing financial risk.
- Accessibility and Mobility: SaaS applications are accessible from anywhere, anytime, on any device. Empower your remote workforce and collaborate effortlessly with global teams, all thanks to the cloud.
- Security and Updates: Gone are the days of manually patching and updating software. SaaS providers handle security and maintenance, ensuring your platform is always protected and up-to-date with the latest features.
- Focus on Your Core Business: Let the experts handle the software! With SaaS, you can offload IT concerns and dedicate your resources to what you do best – running your business.
The SaaS landscape is diverse, catering to businesses of all sizes and types. Let’s explore some main scenarios:
- Startups and SMEs: Budget-conscious and agile, you need solutions that grow with you. Opt for general-purpose SaaS platforms like CRM, project management, and HR software, often offered with tiered pricing based on user count.
- Larger Enterprises: You require robust solutions with industry-specific features and customization options. Look for enterprise-grade SaaS platforms with APIs and integrations that fit your complex workflows.
- Specific Needs: Don’t settle for generic solutions. Specialized SaaS platforms cater to niche industries like healthcare, logistics, or legal services. Look for industry-specific features and compliance certifications.
The Future of SaaS:
The SaaS market is booming, with constant innovation and emerging trends. Expect increased use of AI and machine learning within SaaS platforms, personalized user experiences, and even more emphasis on data security and privacy.
Ready to Make the Switch?
LITSLINK, a leading US software development company, specializes in crafting top-quality SaaS solutions. They understand the unique needs of SME businesses and can help you leverage the power of SaaS to boost your operations and reach new heights.
A Recap
As one can see from the PaaS, IaaS, and SaaS definitions provided above, all three are the models of cloud service provision – a buzzword in modern e-commerce. Each of them has its peculiarities, pros, and cons, and each comes with specific requirements as to its use and the degree of user involvement in the process of software development, management, and upgrade. Choosing your ideal cloud computing model depends on the degree of involvement and control you would like to have, as well as the relative risks and benefits each of them provides.