Imagine billions of tiny robots, constantly traversing the vast landscape of the internet, meticulously indexing every nook and cranny. These industrious bots aren’t figments of a sci-fi film; they’re web crawlers, the unsung heroes behind search engines, data analysis, and countless other internet functions. But have you ever stopped to wonder: what exactly is a web crawler, and how does it operate?
Did you know the average web crawler processes over 100 billion web pages per day, that’s more than 11,000 per second! And these tireless bots are responsible for creating the indexes used by search engines like Google, allowing you to instantly find information within this massive digital library. But how do they manage this seemingly Herculean task?
In this article, we’ll uncover their secrets, demystifying their intricate operations and unveiling their impact on the internet we use every day.
Contents
- What Is a Web Crawler and Indexing?
- How Does a Web Search Work?
- How Does a Web Crawler Work?
- What Are the Main Web Crawler Types?
- What Are Examples of Web Crawlers?
- What Is a Googlebot?
- Web Crawler vs Web Scraper — What Is the Difference?
- Custom Web Crawler — What Is It?
- Wrapping Up
What Is a Web Crawler And Indexing?
Let’s start with a web crawler definition:
A web crawler (also known as a web spider, spider bot, web bot, or simply a crawler) is a computer software program that is used by a search engine to index web pages and content across the World Wide Web.
Indexing is quite an essential process, as it helps users find relevant queries within seconds. The search indexing can be compared to the book indexing. For instance, if you open the last pages of a textbook, you will find an index with a list of queries in alphabetical order and pages where they are mentioned in the textbook. The same principle underlines the search index, but instead of page numbering, a search engine shows you some links where you can look for answers to your inquiry.
The significant difference between the search and book indices is that the former is dynamic, therefore, it can be changed, and the latter is always static.
How Does a Web Search Work?
Before plunging into the details of how a crawler robot works, let’s see how the whole search process is executed before you get an answer to your search query.
For instance, if you type “What is the distance between Earth and Moon” and hit enter, a search engine will show you a list of relevant pages. Usually, it takes three major steps to provide users with the required information for their searches:
- A web spider crawls content on websites
- It builds an index for a search engine
- Search algorithms rank the most relevant pages
Also, one needs to bear in mind two essential points:
- You do not do your searches in real-time as it is impossible
There are plenty of websites on the World Wide Web, and many more are being created even now when you are reading this article. That is why it could take eons for a search engine to come up with a list of pages that would be relevant to your query. To speed up the process of searching, a search engine crawls the pages before showing them to the world.
- You do not do your searches in the World Wide Web
Indeed, you do not perform searches in the World Wide Web but in a search index and this is when a web crawler enters the battlefield.
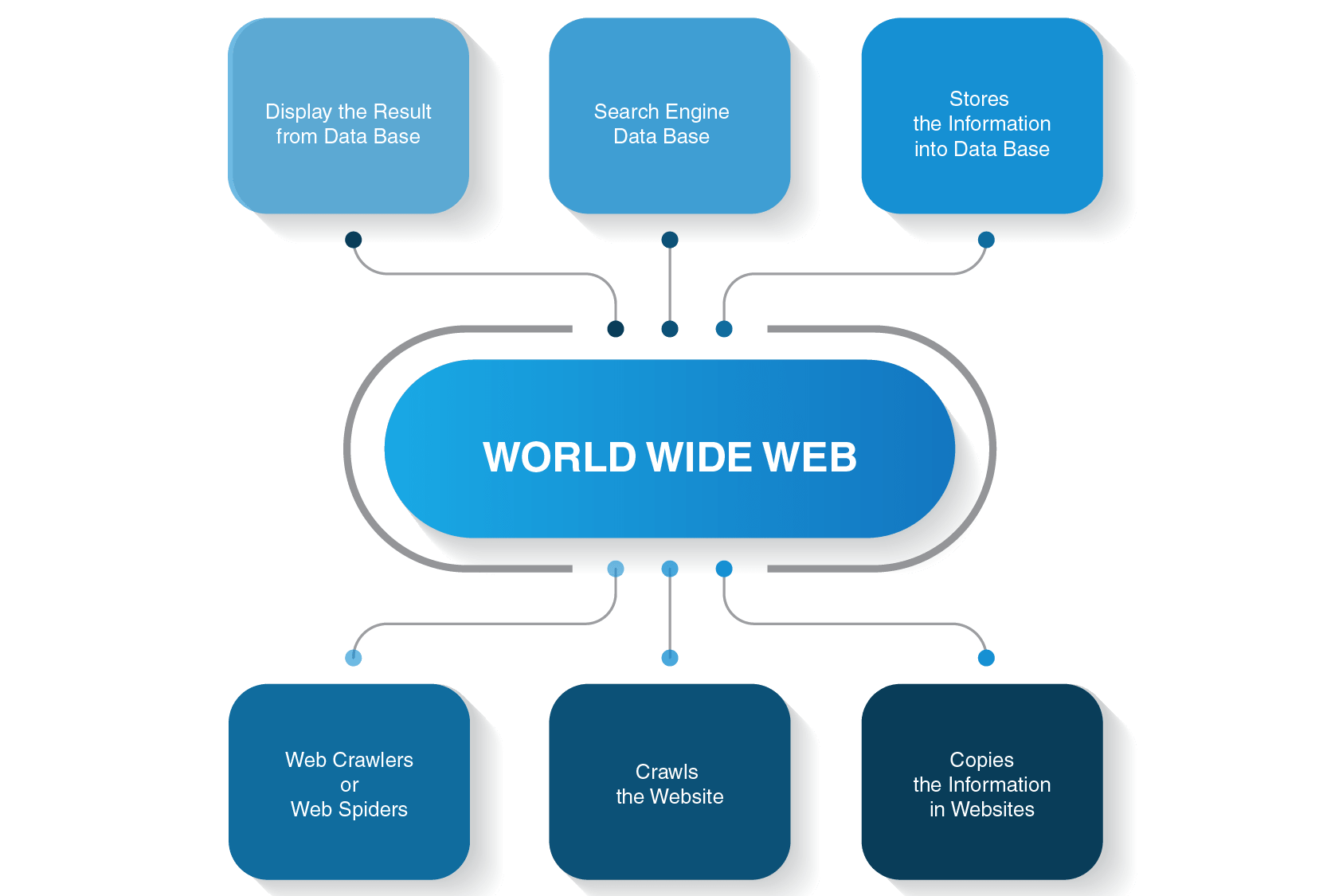
How Does a Web Crawler Work?
There are many search engines out there: Google, Bing, Yahoo!, DuckDuckGo, Baidu, and many others. Each of them uses its spider bot to index pages.
They start their crawling process from the most popular websites. The primary purpose of web crawlers is to convey the gist of what each page’s content is all about. Thus, web spiders seek words on these pages and then build a practical list of these words that will be used by a search engine next time when you want to find information about your query. This process is sometimes referred to as list crawling.
All pages on the Internet are connected by hyperlinks, so site spiders can discover those links and follow them to the next pages. Web bots only stop when they locate all content and connected websites. Then they send the recorded information to a search index, which is stored on servers around the globe. The whole process resembles a real-life spider web where everything is intertwined.
Crawling does not stop immediately once pages have been indexed. Search engines periodically use web spiders to see if any changes have been made to pages. If there is a change, the index of a search engine will be updated accordingly.
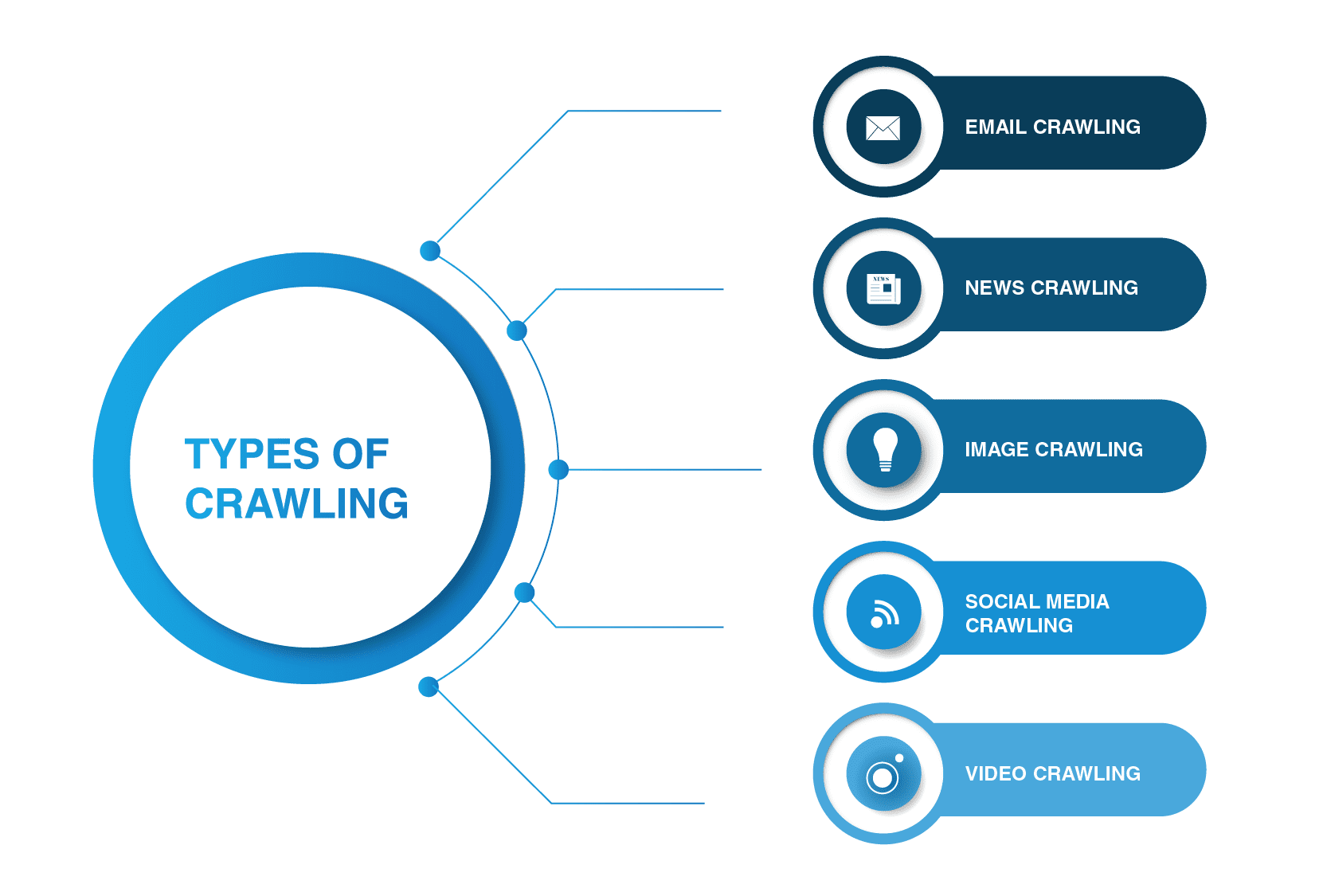
What Are the Main Web Crawler Types?
Web crawlers are not limited to search engine spiders. There are other types of web crawling out there.
- Email crawling
Email crawling is especially useful in outbound lead generation as this type of crawling helps extract email addresses. It is worth mentioning that this kind of crawling is illegal as it violates personal privacy and can’t be used without user permission.
- News crawling
With the advent of the Internet, news from all over the world can be spread rapidly around the Web, and extracting data from various websites can be quite unmanageable.
There are many web crawlers that can cope with this task. Such crawlers are able to retrieve data from new, old, and archived news content and read RSS feeds. They extract the following information: date of publishing, the author’s name, headlines, lead paragraphs, main text, and publishing language.
- Image crawling
As the name implies, this type of crawling is applied to images. The Internet is full of visual representations. Thus, such bots help people find relevant pictures in a plethora of images across the Web.
- Social media crawling
Social media crawling is quite an interesting matter as not all social media platforms allow it to be crawled. You should also bear in mind that such type of crawling can be illegal if it violates data privacy compliance. Still, there are many social media platform providers that are fine with crawling. For instance, Pinterest and Twitter allow spider bots to scan their pages if they are not user-sensitive and do not disclose any personal information. Facebook and LinkedIn are strict regarding this matter.
- Video crawling
Sometimes it is much easier to watch a video than read a lot of content. If you decide to embed YouTube, Soundcloud, Vimeo, or any other video content into your website, it can be indexed by some web crawlers.
What Are Examples of Web Crawlers?
A lot of search engines use their own search bots. For instance, the most common web crawlers examples are:
Amazon web crawler Alexabot is used for web content identification and backlink discovery. If you want to keep some of your information private, you can exclude Alexabot from crawling your website.
Yahoo crawler Yahoo! Slurp Bot is used for indexing and scraping web pages to enhance personalized content for users.
Bingbot is one of the most popular web spiders powered by Microsoft. It helps a search engine, Bing, to create the most relevant index for its users.
DuckDuckGo is probably one of the most popular search engines that do not track your history and follow you on whatever sites you are visiting. Its DuckDuck Bot web crawler helps to find the most relevant and best results that will satisfy a user’s needs.
Facebook also has its crawler. For example, when a Facebook user wants to share a link to an external content page with another person, the crawler scrapes the HTML code of the page and provides both of them with the title, a tag of the video, or images of the content.
This crawler is operated by the dominant Chinese search engine − Baidu. Like any other bot, it travels through a variety of web pages and looks for hyperlinks to index content for the engine.
French search engine Exalead uses Exabot for indexation of content so that it can be included in the engine’s index.
What Is a Googlebot?
As it was stated above, almost all search engines have their spider bots, and Google is no exception. Googlebot is a Google crawler powered by the most popular search engine in the world, which is used for indexing content for this engine.
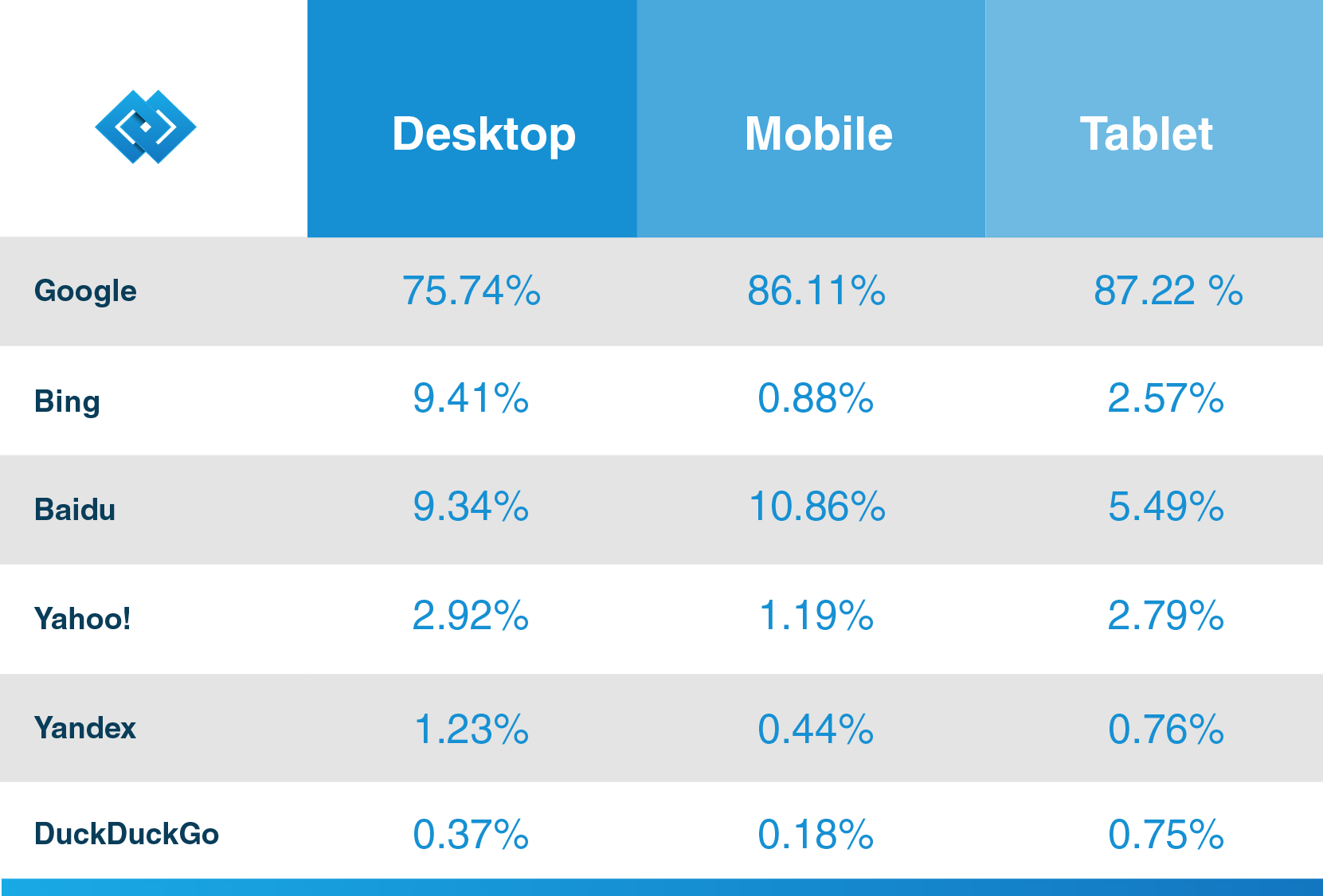
As Hubspot, a renowned CRM vendor, states in its blog, Google has more than 92.42% of the search market share, and its mobile traffic is over 86%. So, if you want to make the most out of the search engine for your business, find out more information on its web spider so that your future customers can discover your content thanks to Google.
Googlebot can be of two types — a desktop bot and a mobile app crawlers, which simulate the user on these devices. It uses the same crawling principle as any other web spider, like following links and scanning content available on websites. The process is also fully automated and can be recurrent, meaning that it can visit the same page several times at non-regular intervals.
If you are ready to publish content, it will take days for the Google crawler to index it. If you are the owner of the website, you can manually speed the process by submitting an indexing request through Fetch as Google or updating your website’s sitemap.
You can also use robots.txt (or The Robots Exclusion Protocol) for “giving instructions” to a spider bot, including Googlebot. There you can allow or disallow crawlers to visit certain pages of your website. However, keep in mind that this file can be easily accessed by third parties. They will see what parts of the site you restricted from indexing.
Web Crawler vs Web Scraper — What Is the Difference?
Many people use the terms “web crawler” and “web scraper” interchangeably, but there’s a crucial distinction between the two. While web crawlers primarily collect metadata like tags, headlines, and keywords, web scrapers “steal” content from a website to publish it elsewhere.
Scrapers are also used to extract specific data, such as stock market trends or Bitcoin prices, from websites. In more advanced setups, developers often rely on rotating residential proxies like GoProxies to spread requests across IPs and reduce rate limits, improving access to target websites with strict anti-bot measures. Crawling your own website for indexing purposes is legal, but scraping content from other websites without permission is against the law.
| Feature | Web Crawler | Web Scraper |
| Primary Goal | Discover and index web pages | Extract specific data from web pages |
| Focus | Breadth – finding new pages and indexing the web | Depth – extracting targeted data from specific pages |
| Output | Sitemap or index used for search engines, research, or analysis | Structured data like product prices, news articles, or social media content |
| Methods | Follows hyperlinks, obeys robots.txt, prioritizes efficiency | May ignore hyperlinks, bypasses robots.txt, emphasizes accuracy |
| Frequency | Regularly revisits pages to capture changes | May only visit pages once |
| Legality | Ethical considerations are crucial, robots.txt must be respected | Must comply with ethical and legal guidelines, respecting websites’ terms and conditions |
| Applications | Search engines, website monitoring, academic research | Market research, price comparison, and sentiment analysis |
Custom Web Crawler — What Is It?
A custom web crawler is a bot that is used to cover a specific need. You can build your spider bot to cover any task that needs to be resolved. For instance, if you are an entrepreneur, marketer or any other professional who deals with content, you can make it easier for your customers and users to find the information they want on your website. You can create a variety of web bots for various purposes.
If you do not have any practical experience in building your custom web crawler, you can always contact a software development service provider that can help you with it.
Wrapping Up
Website crawlers are an integral part of any major search engine that is used for indexing and discovering content. Many search engine companies have their bots, for instance, Googlebot is powered by the corporate giant Google. Apart from that, there are multiple types of crawling that are utilized to cover specific needs, like video, image, or social media crawling.
Taking into account what spider bots can do, they are highly essential and beneficial for your business because web crawlers reveal you and your company to the world and can bring in new users and customers.
If you are looking to create a custom web crawler, contact LITSLINK, an experienced web development services provider, for more information.